كبار مصنعي قوالب صب الزنك في الصين والعالم
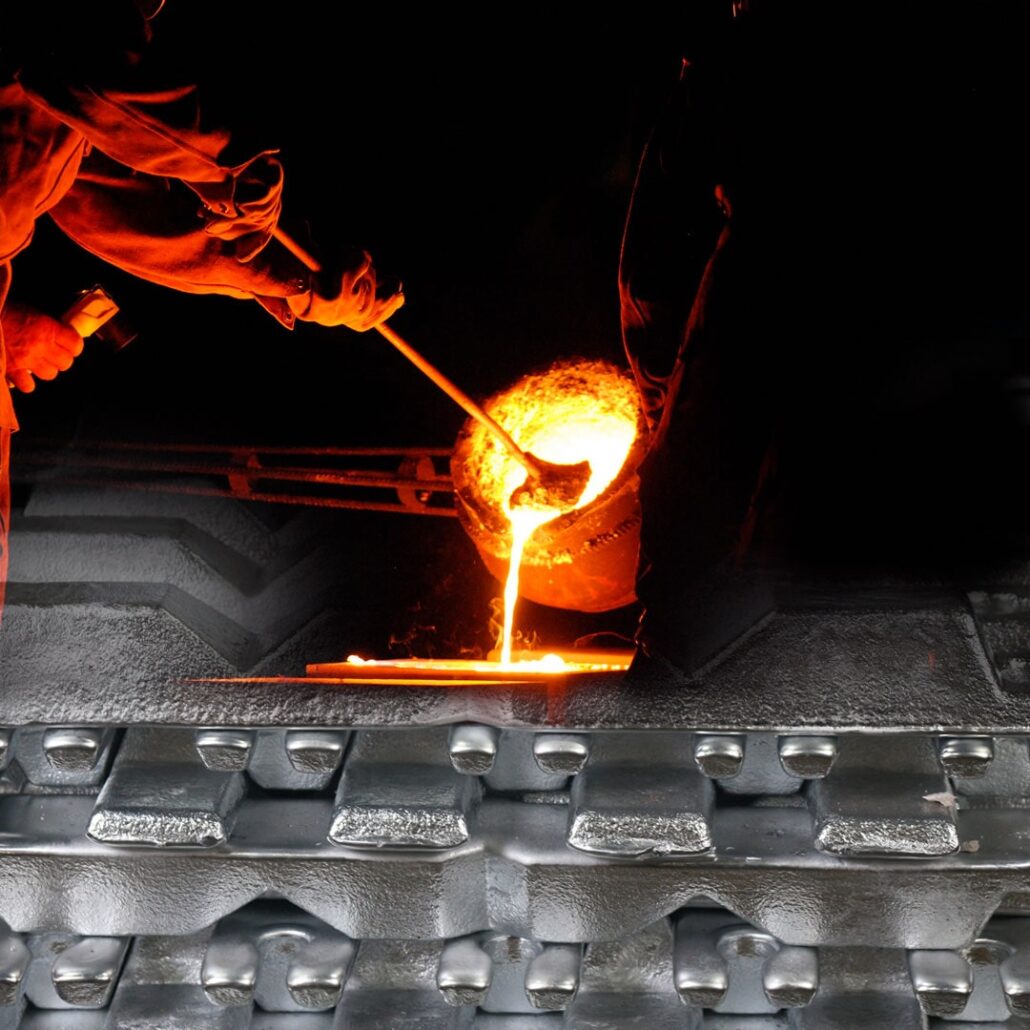
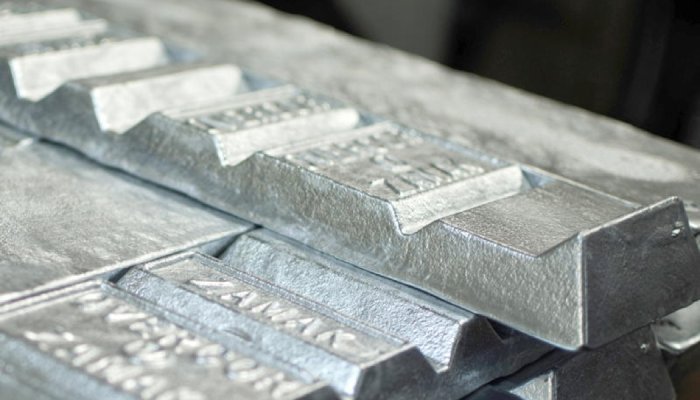
مُصنِّع قوالب الصب بالقالبZinc is thus a steadily growing material as zinc die cast manufacturers due to zinc’s superior strength and dimensionally stable, plus extremely castable properties. The automotive and electronics industries, consumer goods and hardware industries, use zinc alloys very much. Due to their ability to offer components at a low price, with very good surface finishes and little machining, and a high production efficiency, firms that can provide zinc alloy die casting parts are specialized in this area. However, China has many advanced production centers and therefore still dominates the global die casting market. Chinese manufacturers can also offer advanced manufacturing techniques and rapid turnarounds, as well as high capacity. On the other hand, the U.S, Germany, and many other countries’ zinc die casting companies have a high-quality standard, a great innovative approach, and rich experience in the niche market. Here is some of the best zinc die casting manufacturers from the Chinese side of Sincere Tech, GC Precision Mould and CNM Tech alongside the top American firms as DyCast Specialties Corporation. Each entry describes Company’s capabilities, quality commitments, the very good reasons it is the preferred partner in the die casting industry, etc. What is Zinc Die Casting? Zinc Die Casting is the process by which molten zinc alloy is forced under high pressure into a finely machined die (mold) to make a partially hidden combination of intricate work, delicate embellishment, and fine appearance finishing. It is part of the die casting family, a family of processes in which molten metal is injected into a mold cavity directly under high pressure. The use of zinc as the material exploits the fact that zinc is a good castable material with good corrosion, and high strength retention properties at somewhat low temperatures. Zinc die casting is generally accomplished with the use of high-pressure machines that have the metal charged at high pressure and pushed into molds for a quick and reliable process of production of high-accuracy parts with pressure exceeding 10,000 psi. Zinc die casting is the most versatile method to produce small to medium-sized components, and it is possible to produce intricate shapes with tight tolerances. Zinc die casting parts are widely used in all automotive, electronics, telecommunications, and hardware industries, which require extra processing of having to be machined, polished, plated, or painted. Because of this, manufacturers can minimize waste and produce high quantities of parts, and thus, become economical for mass production. Zinc die cast also possesses good mechanical properties with easy, secondary operations (threading and drilling and excellent dimensional stability as well. In addition, it has the characteristic of a low melting point compared to other metals, like aluminum or magnesium, so less energy is needed during the casting process, which makes it an energy-efficient and environmentally friendly material. Benefits of Zinc Die Casting The Benefits of Zinc Die Casting include a family of benefits that make it a top choice to produce highly engineered, strong parts. Here are the key benefits: 1. High Precision and Tight Tolerances Due to the fact that parts with the highest level of detail and complexity, and very close dimensional tolerances can be produced, zinc die casting is very well suited for the part production. Collaboration means that you are able to make products with the same quality, thus reducing the post casting machining. 2. Cost-Effective for High-Volume Production In many cases, new technologies exist for zinc die casting that provide cheap means of its production in unlimited amounts. This does provide for reuse of the molds, and for the fast casting speed, therefore the cost per unit decreases with increase in production volume, contributing to the low-cost solution for mass production. 3. Excellent Mechanical Properties Zamak alloys possess good strength, stiffness, and durability and can be die-cast. Zinc die casting parts possess good wear and corrosion resistance and are thus the ideal choice for application areas where very good longevity is required, in a wide range of areas of application accordingly including the automotive and hardware as well as in electronics industries. 4. Superior Surface Finish Zinc die castings have smooth, high-quality surface finishes, and this may aid in reducing the need to further finish with a polish or paint. “It also improves part aesthetics (more so in consumer products and decorative applications) and part flexibility; it enables greater rigidness for a more rigid base to accept more time-consuming, less rigid, and more expressive routing.” 5. Ease of Secondary Operations Zinc die castings are easily machinable, threadable, assemble assembleable. Also, secondary operations such as drilling, tapping, or threading of zinc die-cast parts are easily made fast. 6. Low Melting Point and Energy Efficiency The low casting energy of zinc (low melting point 419 °C) helps in reducing energy. Although the mentioned competitor metals with higher melting points, such as aluminum or magnesium, cannot compete in terms of energy efficiency or environmental friendliness with zinc die cast. 7. Design Flexibility By nature, it produces complex and intricate shapes which would be very hard, if not impossible, to replicate using some other method. Zinc die casting also realizes the inclusion of thin walls, undercuts, etc., without loss of strength. 8. Corrosion Resistance Zinc alloys do, however, possess excellent corrosion resistance in harsh environments. Zinc die-cast parts are used in outdoor applications and products exposed to moisture for a long and reliable performance in outdoor applications. 9. Material Strength and Durability Zinc die casting can tolerate good material strength, about appearance, and mechanical stress. Especially in applications requiring high durability, such as auto, component, hardware, and tooling, it is robust when used alone. 10. Recyclability Secondly, zinc die casting is 100% recyclable with no degradation of properties and hence is an environmentally friendly option. Recycled zinc can be used in the casting process to decrease waste materials and embark upon a circular economy. Overall, the use of zinc die casting is great for its strength, precision, and cost, and long-term durability ensures that you can use zinc die casting for many different industries