شركات صب الألومنيوم بالقالب في الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية
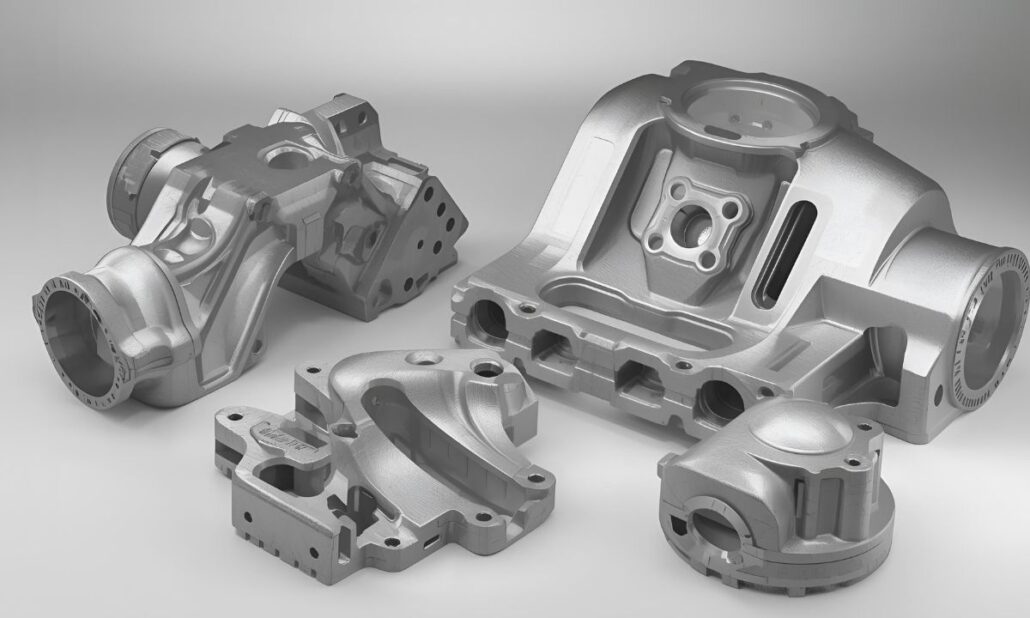
صب القوالب الألومنيوم, شركات صب القوالب, شركة صب القوالبيُعد صب الألومنيوم بالقالب الآن أحد أضمن إجراءات الإنتاج وأكثرها اقتصادية في الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية، خاصةً للمصنعين الذين يحتاجون إلى المتانة وطول العمر والدقة. ويتم ذلك عن طريق الحقن بالضغط العالي للألومنيوم المصهور في مصبوبات الفولاذ، وهذا ينتج أجزاء ليست خفيفة الوزن فحسب، بل دقيقة الأبعاد ومتينة أيضًا. إن هذه القوة والوزن الخفيف هي التي تجعل من مصبوبات الألومنيوم المادة المفضلة في صناعة السيارات والفضاء والإلكترونيات والآلات الصناعية والسلع الاستهلاكية. يضم سوق الولايات المتحدة بعضاً من أكثر صناعات صب قوالب الألومنيوم رسوخاً في جميع أنحاء العالم في شكل شركات تصنيع كبيرة ذات حضور عالمي إلى شركات صغيرة ومتخصصة متخصصة في الأجزاء المخصصة والتطبيقات المتخصصة. وتعد هذه الشركات حاسمة للغاية في دعم الصناعة الرئيسية من خلال توريد قطاعات الصناعة مثل كتل المحركات، وأغطية ناقل الحركة، والحاويات الإلكترونية، والأجزاء الهيكلية. وقد اكتسبت الشركات المصنعة التي تتخذ من الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية مقرًا لها سمعة موثوقيتها ومنتجاتها المبتكرة في العالم من خلال تقنياتها عالية الجودة وشهاداتها وتركيزها على جودة المنتجات. وقد شهد الاتجاه في السنوات القليلة الماضية زيادة هائلة في الطلب على قطع الألومنيوم المصبوب بسبب التطورات الأخيرة في مجال تخفيف وزن السيارات، وإنتاج السيارات الكهربائية، والسعي لتصنيع السيارات الكهربائية والسعي لتصنيع الطاقة بكفاءة. تتبنى الشركات الأمريكية الأتمتة والمسبوكات المستدامة والسبائك المتفوقة لتحقيق نتائج عالية لتلبية هذه المتطلبات. تسرد هذه المقالة بعضًا من أفضل مصنعي قوالب صب الألومنيوم في الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية وإنجازاتهم وإمكاناتهم ومساهماتهم في الصناعة المعاصرة. لا يهم ما إذا كنت تحصل على قطع غيار لتنفيذ عملية تصنيع واسعة النطاق أو تطبيق عالي التقنية، فإن هؤلاء المصنعين هم تجسيد لأرقى التقنيات الأمريكية في مجال صب الألومنيوم بالقالب. ما هو صب الألومنيوم بالقالب؟ الصب بالقالب المصنوع من الألومنيوم هو تقنية إنتاج يتم فيها الضغط العالي على الألومنيوم المصهور في قالب فولاذي يُشار إليه أيضًا بالقالب. عندما يبرد المعدن ويتصلب يتم فتح القالب وإخراج الجزء المكتمل. هذه هي العملية التي يمكن للمصنعين من خلالها إنشاء مكونات قوية وخفيفة ومفصلة للغاية مع مستوى عالٍ من الدقة في الأبعاد والتشطيبات السطحية الملساء. إن حقيقة أن عملية صب الألومنيوم بالقالب يمكن أن تنتج أشكالاً معقدة قد يكون إنتاجها صعباً أو مكلفاً باستخدام عمليات التصنيع الأخرى هي الفائدة الرئيسية. ويستخدم على نطاق واسع في تصنيع أجزاء مثل كتل المحركات، وأغلفة ناقل الحركة، والحاويات الإلكترونية، والمشتتات الحرارية والمكونات الهيكلية. يتميز قالب الصب بالقالب المصنوع من الألومنيوم بالعديد من المزايا الرئيسية: وبفضل نقاط القوة هذه، برز صب الألومنيوم بالقالب كبديل أفضل في الصناعات التي تتطلب مكونات عالية الجودة يمكن الاعتماد عليها وفعالة لتتناسب مع احتياجاتها التقنية والاقتصادية. أفضل شركات صب الألومنيوم بالقالب في الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية 1. Dynacast International تعد شركة Dynacast International واحدة من أفضل الشركات المعروفة في مجال الصب الدقيق للقالب على مستوى العالم. تتمتع الشركة بعقود من الخبرة في إنتاج المكونات الصغيرة والمعقدة باستخدام سبائك الألومنيوم والزنك والمغنيسيوم. وهي بارعة في إنتاج المكونات ذات التفاوتات الصارمة والميزات المعقدة التي تحتاجها صناعات السيارات والإلكترونيات الاستهلاكية والاتصالات والأجهزة الطبية. وكونها شركة عالمية يعني أيضاً أن Dynacast قادرة على خدمة الشركات الصغيرة والشركات متعددة الجنسيات بمرونة وابتكارات وجودة لا تختلف بين المشاريع. 2. صناعات بيس بعد أن أصبحت أكبر شركات صب القوالب في أمريكا الشمالية، اكتسبت صناعات بيس سمعة جيدة في تقديم حلول متكاملة. وتشمل مجموعة خدماتها التصاميم والدعم الهندسي، والمسبوكات بالقالب، والتشغيل الآلي، والتشطيب السطحي، والتجميع النهائي؛ فهي تقدم حلًا شاملاً للعملاء في قطاعات السيارات والصناعات والصناعات الاستهلاكية. يمكن التعامل مع المشاريع ذات الحجم الكبير والمشاريع المخصصة بسبب حجم عملياتهم. كما تتبع شركة Pace ثقافة توظيف الأموال في التكنولوجيا الحديثة والممارسات المستدامة بحيث تكون قادرة على الحفاظ على قدرتها التنافسية في الصناعة سريعة التغير. 3. Ryobi Die Casting (الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية), Inc. ريوبي هي علامة تجارية مشهورة في قطاع الصب بالقالب في العالم، ولها حضور كبير في الولايات المتحدة. تتركز عملياتها في الولايات المتحدة على مكونات الألومنيوم المصبوبة بالقالب على نطاق متوسط إلى كبير الحجم، خاصةً في قطاع السيارات. تقوم شركة ريوبي بتصنيع كتلة المحرك، ومبيت ناقل الحركة، والأجزاء الهيكلية التي تحتاجها لتكون متينة ودقيقة. وقد استخدمت الشركة أحدث التقنيات المتطورة وإدارة الجودة مما جعلها تصبح المورد المفضل لكبار مصنعي السيارات في العالم. 4. شركة Gibbs Die Casting Gibbs Die Casting، الشركة الرائدة الأخرى في السوق الأمريكية ومقرها في هندرسون بولاية كنتاكي. تتخصص الشركة في مصبوبات الألومنيوم والمغنيسيوم في صناعة السيارات، خاصةً علب ناقل الحركة وأجزاء قطار الطاقة. تركز جيبس تركيزاً كبيراً على الابتكار حيث يتم استخدام الأتمتة وتقنيات التصنيع المتطورة لضمان معايير عالية من الكفاءة وجودة العمل. كما تدمج الشركة مفهوم الاستدامة في أعمالها من خلال الحد من الهدر وتشجيع الممارسات التجارية الصديقة للبيئة. 5. شركة Apex Aluminum Die Casting Co., inc. تقع شركة Apex Aluminium Die Casting في ولاية أوهايو وتستخدم في صناعات السيارات والإلكترونيات والأجهزة المنزلية. وتتمتع الشركة بسمعة طيبة في العمل مع حصص الإنتاج متوسطة الحجم، مما يجعلها الخيار الأمثل مع الشركات التي تتطلب جودة إنتاج ثابتة ولكنها لا تتطلب القوى الهائلة للمستوردين الكبار. يهتم فريق أبيكس برضا العملاء وموثوقية الخدمة والهندسة والدقة في التصنيع. وقد أثبتوا أنفسهم كشريك موثوق به لعدد من الشركات الأمريكية بسبب سمعتهم الجيدة في تقديم نتائج ثابتة. 6. شركة KenWalt Die Casting Company يقع مقر شركة KenWalt Die Casting في كاليفورنيا ولديها أكثر من عدة عقود من الخبرة في إنتاج مصبوبات القوالب؛ الألومنيوم والزنك. تركز الشركة أيضًا على الأعمال المصممة حسب الطلب وتخدم صناعات كل من المعدات الصناعية والسلع الاستهلاكية. تتميز شركة KenWalt بأنها شركة تتعاون بشكل وثيق مع العميل أثناء