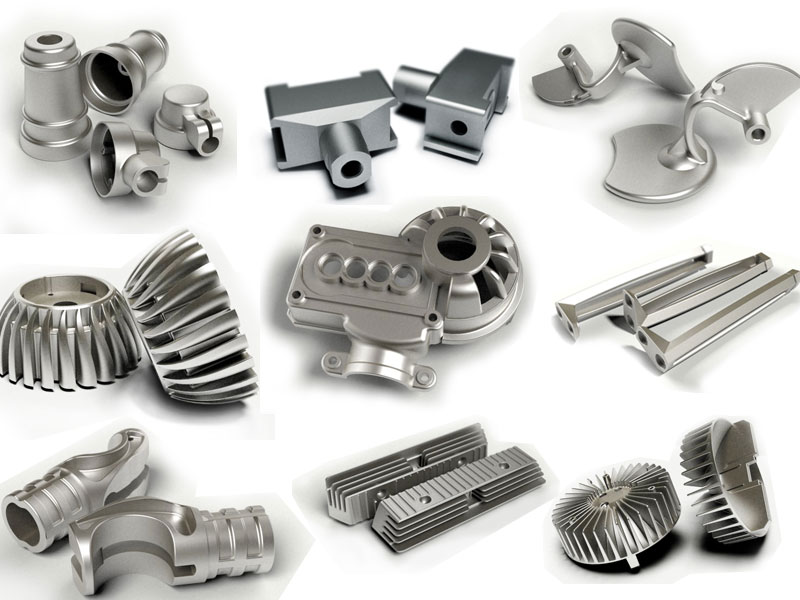
Χύτευση αλουμινίου: Αλουμινίου: Ένας ολοκληρωμένος οδηγός
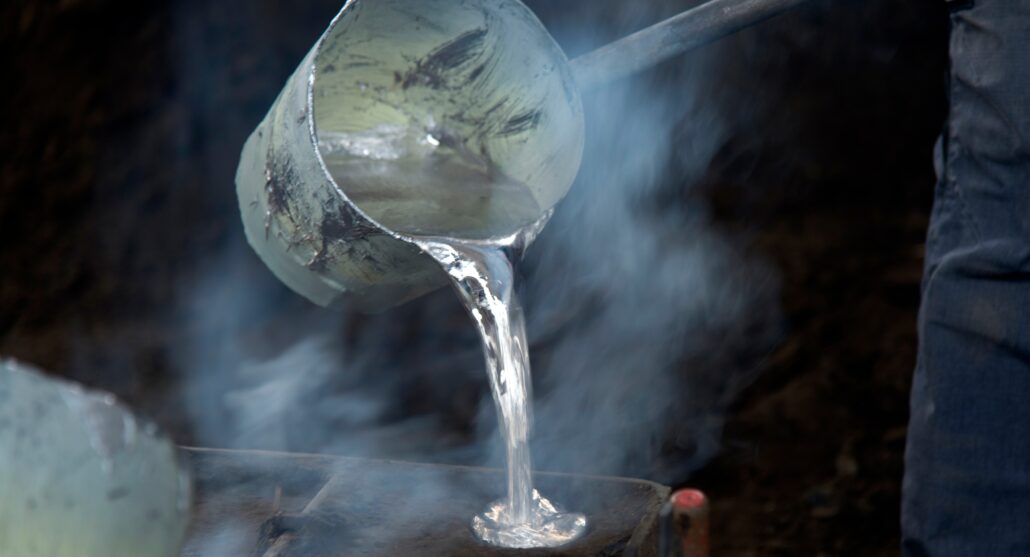
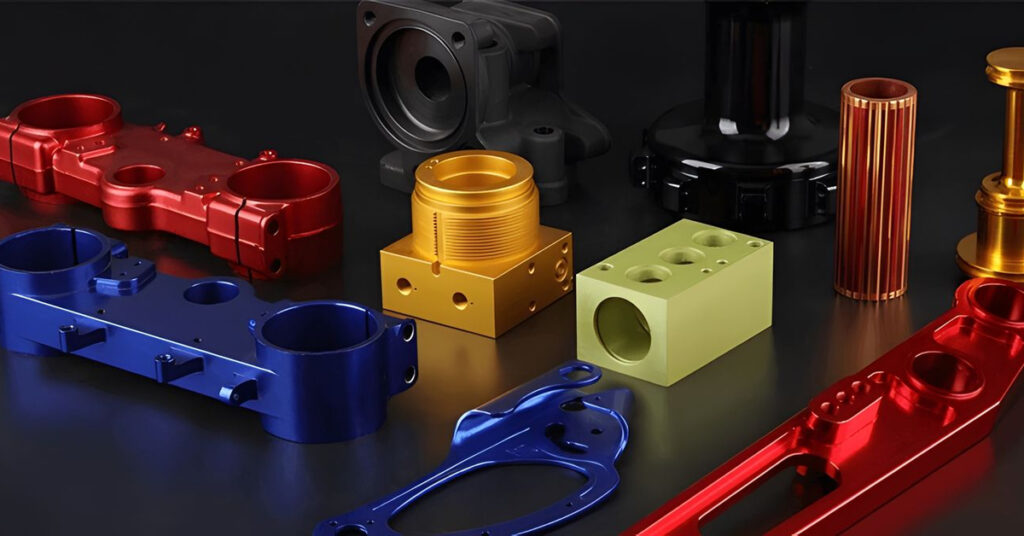
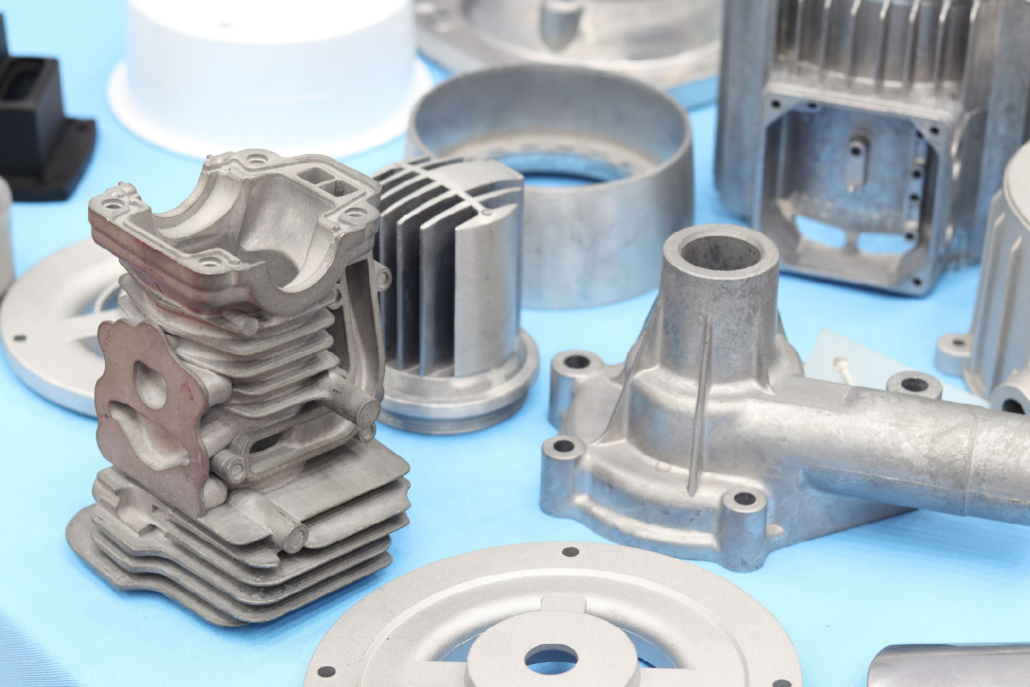
καλούπια χύτευσης αλουμινίουCurrent industries extensively use aluminium because of its strength combined with its low weight along with its ability to resist heat effectively. The production of aluminium components achieves its best results through the casting aluminium process. The procedure enables users to produce intricate complex shapes which work perfectly for industrial needs and commercial environments. Manufacturers widely employ the casting aluminum method to create complex and resilient components by pouring molten aluminum into designed moulds. Produced components through casting aluminium are widely used across the automotive, aerospace, construction and cookware sectors because aluminium offers excellent thermal conductivity together with lightweight construction and corrosion resistance properties. The essential basis for understanding casting aluminium demands an initial definition of what cast aluminium represents. Castaluminiumm represents metaaluminiumum processed through thermal melting followed by mould filling which results in its transformation into precise configurations. Industrial producers use this method to achieve precise detailed designs which suit engine parts together with machinery parts as well as heat exchangers. Cast aluminium stands out because its strength-to-weight ratio outperforms every other metal thus making it suitable for applications that require lightweight construction. Three main techniques include die casting, sand casting and investment casting that manufacturers use to perform the casting aluminium process with their specific advantages. Die casting performs high-speed precise processing that matches well with mass production but sand casting delivers versatile low-cost benefits suitable for low-volume manufacturing. The investment casting method can deliver both high accuracy and elaborate details in finished products. Knowledge about cast aluminium composition along with manufacturing methods enables industry professionals to pick suitable production systems. Global industries choose to castg aluminium as their standard procedure because it provides lightweight durability with corrosion protection in addition to cost efficiency. What Is Cast Aluminum? Aluminium becomes cast aluminium when manufacturers melt the aluminium metal to pour it into specific moulds for product creation. The unique aspect of aluminium casting enables manufacturers to create complex shapes while reducing material waste better than machine orextrudedealuminiumm methods. What purposes does aluminum casting serve? Different industries use cast aluminum as a primary material to create automotive parts and cookware together with furniture, machinery and aerospace components. Through its production method the product results in strong yet lightweight performance which makes it ideal for efficiency and durability applications. Key Characteristics of Cast Aluminum: Step-by-Step Guide to Casting Aluminum Working with molten aluminium needs severe safety precautions because it creates danger when mishandled. Every step should begin with putting on gloves along with heatproof clothes and face protection. This manual presents a simple method of aluminum casting that protects both workers and equipment. These specific die-casting steps work the same way in other aluminium casting processes. Step 1: Begin By Creating The Mold For Your Project Design The beginning of aluminium casting starts with developing and readying the mould design. The mould selection process controls how the casted aluminium item looks and behaves. Cutting tools must match the chosen mold material which could be sand, steel, ceramic, plaster or aluminum. The mould design must precisely match all details and requirements of the final aluminium product. To produce precise molds manufacturers use CAD system software. The software helps designers build an exact 3D representation of their product before making it. After the digital design is ready CNC machines accurately make and form the mold. The user applies a release agent to the inside of the mould before production starts. The coating applied to the mold prevents aluminum from bonding to it so the cast part can be easily removed. After application of the coating the mold is tightly closed before continuing. Step 2: Melting the Aluminum The following step is to heat the aluminum until it liquefies. The metal reaches melting temperature of 660 degrees Celsius (1220°F) very fast due to its low melting point.The furnace heats up aluminum metal to its melting temperature before electricity or gas power is used to transform it into a fluid substance. The liquid aluminum moves from the furnace to a storage area where it remains usable until deployment into the mold. Step 3: We pour the melted aluminum into the mold The ready molten aluminium can flow smoothly into the mould since its temperature is optimal. Our team pours the aluminium with exact movements to avoid creating defects from trapped air in the finished item. The gate system is specially designed to let aluminium metal flow smoothly into the mould’s cavity. Once the mould reaches its capacity all additional aluminum drains out. After pouring ends the mold stays untouched as the metal starts to cool and harden. Step 4: Cooling and Solidification Casting aluminum needs proper temperature reduction and solidification steps. The casting process takes a period that depends on how thick and intricate the part is.Proper temperature reduction steps are needed to create parts with the needed strength and capacity. A steady temperature needs to stay constant during metal cooling to prevent parts like warping or internal stress from developing.Manufacturers employ cooling tools like air, water and furnace temperature control during aluminum solidification. Step 5: After Solidification the Casting Leaves the Mold When aluminum solidifies completely we extract the casting out of its mold. We need to cut away the leftover material known as flash sprues from the product. Included finishing actions to produce the desired outcome are water cooling and heating control in the furnace process. We use machining tools to create exact dimensions after product processing. To make surface texture easy to work with. Using polishing or coating techniques makes aluminum surfaces shine better while increasing their resistance to wear. The casting of aluminum production ends when quality finishing techniques produce a ready-to-use item. Great! Your existing steps explain how aluminium castings are made yet producers mostly complete their procedure using more steps. Several additional methods help enhance the quality of final cast aluminum parts. Step 6: heat treatment improves metal quality though it is optional. Manufacturers enhance aluminum mechanical properties by implementing a heat treatment process after casting ends.