The cold chamber die casting process is initiated by first ladling molten metal into a separate injection chamber and then forcing it out into a steel mould. This process deals with high melting alloys such as aluminium, copper and magnesium. It is a tight-tolerance, high-pressure production process found in the automotive, electronics, and industrial parts production.
Πίνακας περιεχομένων
ΕναλλαγήWhat is cold chamber die casting is and when to use it?
Cold chamber die casting is a high-pressure moulding of metals, which would ruin or corrode a hot-chamber system. Practically, the operators melt the metal in a different furnace. Then they pour the molten metal into an unheated shot sleeve. The metal is forced into the closed mould by a hydraulic plunger with extreme pressure. The section hardens very rapidly, and the die is opened to spurt out the casting. This can be used when the alloy is of high melting temperature or where the alloy would corrode injection components, such as aluminium and copper alloys. The process sacrifices speed of the cycle for the scale and flexibility of the alloy.
Cold Chamber Die Casting Process Step-by-Step
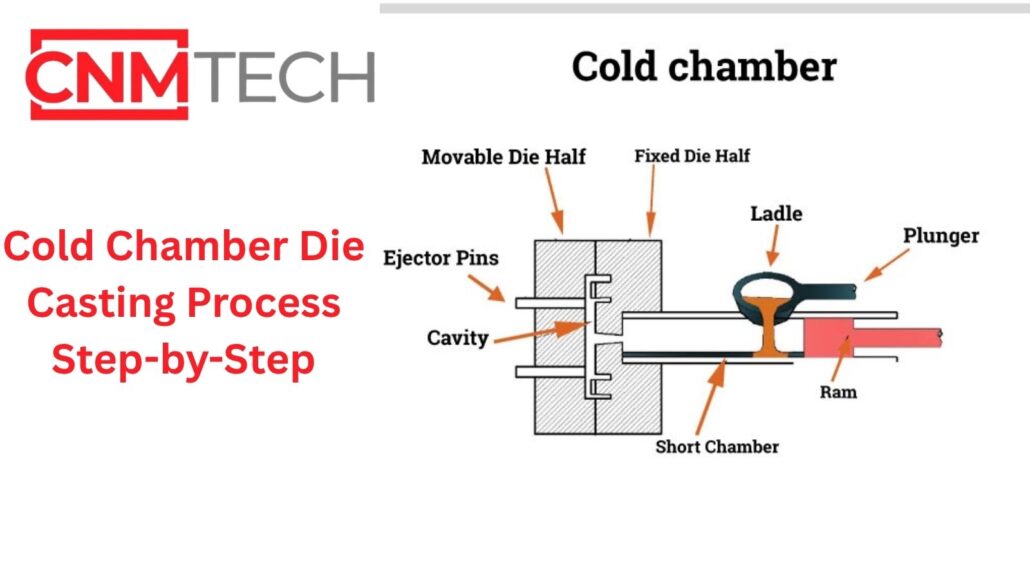
Cold chamber die casting is one of the most reliable techniques for making high-quality metal parts. Every process must be monitored in terms of temperature, pressure and time. Minor variations can impact the surface finish, strength and dimensional accuracy of the end product.
Λιώσιμο του μετάλλου
It starts by melting the metal in a separate furnace. Mostly used are aluminium, magnesium and copper alloys. In the case of aluminium, it is typically 650degC and 750degC. It is necessary to keep the melt clean.
The impurities are eliminated by the operator with the help of fluxing agents and skimming tools. In case some oxide or gas is left, it may introduce defects such as porosity or inclusions in the future.
In high-tech furnaces, a dosing system is the direct connection between the furnace and a die casting machine of China Cold. This guarantees that the temperature and composition of the molten metal are uniform in each shot.
Molten Metal to the Shot Chamber
Then molten metal is poured into the shot chamber or shot sleeve. This may be done manually or automatically.
Manual ladling is easy, less fast and has more chances of entraping air. Automatic ladling systems, in their turn, provide the accurate amounts of metal with low turbulence.
Oxidation and gas inclusion can be prevented by controlling the ladling speed and temperature. Others preheat the shot sleeve a little so that it will not suddenly drop in temperature, to allow the fluidity of injection.
3. Injection into the Die Cavity

A hydraulic plunger is used to inject the high-pressure molten metal into the die cavity once it is in the shot sleeve. This is the fundamental phase of the cold chamber die casting.
Injection pressure varies between 3,000 psi and more than 20,000 psi, depending on the size of the part and the alloy. The injection cycle normally contains two stages:
- Fast fill stage: The plunger is forced very fast to fill the die until the metal begins to harden.
- Intensifying or packing stage: The metal is further pressed in order to make it tight and to remove shrinkage.
The timeliness of these phases is critical. Recent China cold chamber die casting machinery, servo-hydraulic systems automatically regulate pressure and speed of every shot and guarantee homogeneity.
Στερεοποίηση και ψύξη
- When the molten metal is poured into the die, the cooling and solidification start at once.
- The die has internal cooling channels in which water or oil circulates to cool the die effectively.
- To ensure uniform quality, it is necessary to maintain an optimum die temperature between 150 o C and 250 o C.
- When the die is overheated, then cycle times become longer and flash could occur. When it is too cold, the metal can be solidified before filling up the cavity and causing cold shuts or misruns.
- High-tech systems can be capable of thermal simulation and temperature sensors observing hot areas and designing cooling layouts to achieve a uniform distribution of heat.
Opening and Part Ejection Die
Once the metal has solidified, the die is opened by the machine, after which ejector pins or robotic arms take the casting out.
It should be ejected only when fully solidified; otherwise, it is distorted. In complex shapes, there is more than one ejector pin, which guarantees the clean release of the die cavity.
Robots take the parts on the automated lines and place them on conveyors to be trimmed and cooled. This increases handling damage reduction and accelerates production.
Κοπή και φινίρισμα
- After the casting has been ejected, it still includes surplus material runners, gates and flash.
- They are cut off by means of trimming presses, saws, or CNC machines.
- In others, the trimming is automatically done by robotic trimming systems to guarantee uniform production.
- The castings can then be subjected to secondary processes such as machining, drilling, tapping, polishing, anodising or coating after the trimming.
- These measures enhance the accuracy of the dimensions and finish of the part, and call it an assembly or a final inspection.
Inspection and Quality Control
The last one is inspection and quality control. Every casting is inspected to guarantee that it has the necessary tolerances and quality standards.
Popular types of inspection are:
- Callipers/coordinate measuring machine (CMM).
- Graphical checking of fissures, blaze or superficial flaws.
- Tests that do not involve destruction, like X-ray or ultrasonic tests, are used to determine internal porosity.
- Testing of components of engine housings or valves, such as for leaks or pressure.
The machinery of modern China cold chamber die casting is usually equipped with sensors and software which keep track of all the parameters – Melt temperature, injection pressure, and die temperature, which enables quality monitoring in real time.
Optimisation of process and control
The quality of outcomes must rely on controlled quality at each step.
- Operators watch such aspects as the cleanliness of the melt, ladling method, speed of the shot, pressure curve, and temperature of the die.
- Minor scraps may add or cause dimensional errors.
- Automation assists in minimising human error. Repeatability is enhanced and porosity is reduced with the use of servo controls, robotic handling and vacuum systems.
- Routine servicing- cleaning hydraulic lines, inspecting seals, and calibration of sensors is the guarantee of the regularity of machine work.
Safety and Environmental Factors
- The handling of molten metals is hazardous.
- The operators should use heat-resistant gloves, face shields and protective clothes.
- There should be emergency stops, heat shields, and temperature or pressure automatic alarms on machines.
- Modern systems are also energy efficient and waste minimising in terms of the environment.
- Servo-hydraulic systems use less energy. Cooling circuits are water-cooled.
- Certain Chinese cold chamber die casting machines have closed-loop systems, in which heat is reused, and this minimises the carbon footprint.
Usually used materials and alloys.
The use of a cold chamber is preferred in alloys which cannot be utilised in hot-chamber machines. Most common materials used include aluminium alloys, magnesium, copper and a few combinations of zinc andaluminiumm where corrosion of the injection mechanism should be prevented at all costs. In the automotive structural parts, aluminium alloys prevail. Magnesium is applicable in situations where very lightness is an issue. Both alloys have their own melting point, fluidity and shrinkage behaviour, which need to be handled in mould design and process parameters.
Machinery and features – such as the China cold chamber die casting machine choice.
Die casting machines: The Cold chamber die casting machines are made of a robust frame, high pressure injection unit, a hydraulic system and the control electronics. The modern machines provide servo-hydraulics to save energy and enhance control, computer controls to make the shot profiles programmable and integrated auxiliary systems such as die temperature controllers and automatic ladling systems. It is also possible to find China cold chamber die casting machine suppliers that offer a large variety of models and different price ranges in case you are sourcing machines. There are compact models of Chinese manufacturers that fit small shops and large tonnage machines that are appropriate to high-volume production. Chinese constructors tend to package melting and handling equipment to provide a turnkey line as well. Compare machines in terms of check maximum clamping force (tons), volume in the shot, speed control in an injection, die size, and automation.
Essentials of tooling and die design
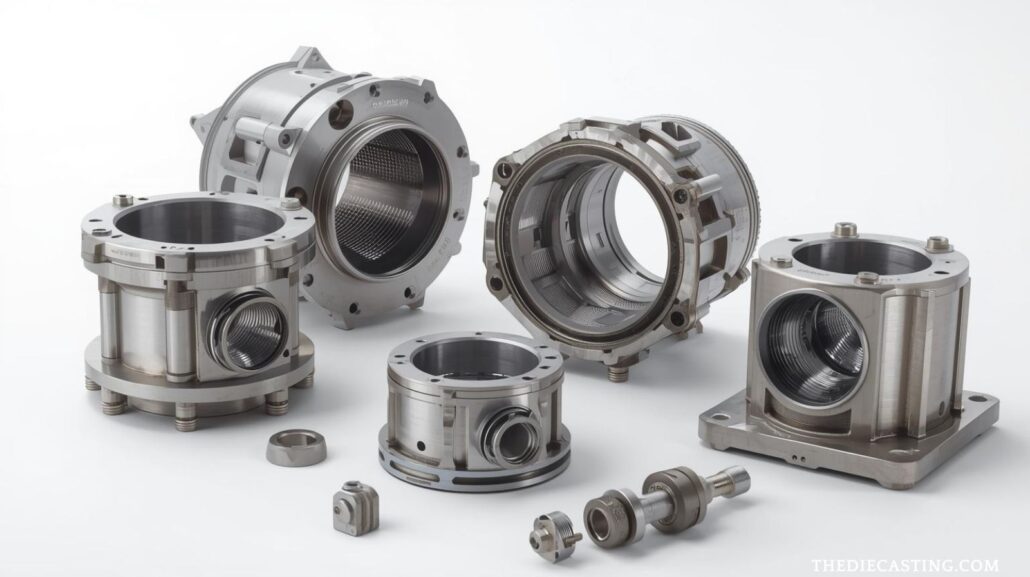

The hardened tool steel is normally die (mould. The design of the die should permit a controlled flow of metals and escaping gaseous air, and gating and runners geometry and cooling channels in order to cool the design rapidly. Notable design issues are the prevention of cold shuts, the reduction of porosity and restraining shrinkage. Danishes, sliders and cores are typical of forming complicated geometries. Good maintenance of the die, such as polishing and shot-blasting between successive runs, increases the life of the tool and maintains the finish of the surface.
Table of quality control
| Model | Δύναμη σύσφιξης | Injection System | Automation Options | Καλύτερα για | Πλεονεκτήματα | Μειονεκτήματα |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longhua LH-400T | 400 tons | Dual hydraulic injection | Optional automatic ladling | Medium-sized aluminum parts | Reliable, easy maintenance, affordable | Manual ladle required |
| LK Group DC700 | 700 tons | Servo-hydraulic control | Automatic ladle + die spray | Large castings and automotive use | Energy efficient, precise | Ακριβό |
| Yizumi DM4000H | 4000 tons | Two-plunger high-pressure | Fully robotic system | Industrial-scale production | Handles large molds, fast | High power consumption |
Uses of Cold Chamber Die Casting
Cold chamber die-casting is a crucial technology in the contemporary industry that needs high precision, sturdy and intricate metal components. Due to its capacity to process metals with high melting points, such as aluminium, copper, and magnesium, it has been used as a desirable production process in vital parts in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and heavy machinery.
Βιομηχανία αυτοκινήτων
One of the automotive industry is a large consumer of cold chamber die-cast components. The process is used in manufacturing parts of an engine block, transmission housings, clutch covers, gear cases, and wheel parts. These components have to survive high mechanical loads, high temperatures and constant vibration. Cold chamber die casting is done to guarantee high standards of dimensions and performance. In this regard, aluminium and magnesium alloys are specifically popular in the industry due to their ability to offer strength even with the low weight of the vehicle, thereby increasing fuel efficiency and handling.
Αεροδιαστημική βιομηχανία
In aerospace production, all the parts should provide a perfect weight, strength and accuracy balance. Cold chamber die casting enables the manufacturing of structural brackets, airframe supports, housings and engine-related parts to great dimensional accuracy. The low fineness of the surface and the interior integrity that this casting technique offers make it very appropriate in aerospace applications, as aerospace parts have to be of high safety and reliability standards.
Βιομηχανία ηλεκτρονικών ειδών
Cold chamber die casting is useful to the electronics industry in the production of complex components with high precision. Electronic device components such as heat sinks, enclosures, connectors, and electronic device housings are normally made of aluminium alloys. These components should have good thermal conductivity, be light and be corrosion-resistant. Die-cast aluminium components are useful in cooling heat effectively, thus enhancing the performance and longevity of the current electronic devices, including computers, LED lights, and communication devices.
Industrial Machinery and Equipment
Pumps, valves, compressors, motor housings, and hydraulic parts of industrial machines are also produced by the use of cold chamber die casting. Such components have to work under extreme conditions, and they need high strength and dimensional precision. The process guarantees uniformity of the wall thickness, good sealing surfaces, and good mechanical characteristics. The reason why manufacturers choose this approach to industrial machinery is that it can be produced in high volumes without losing precision.
Consumer and Energy Applications Consumer and Energy Applications
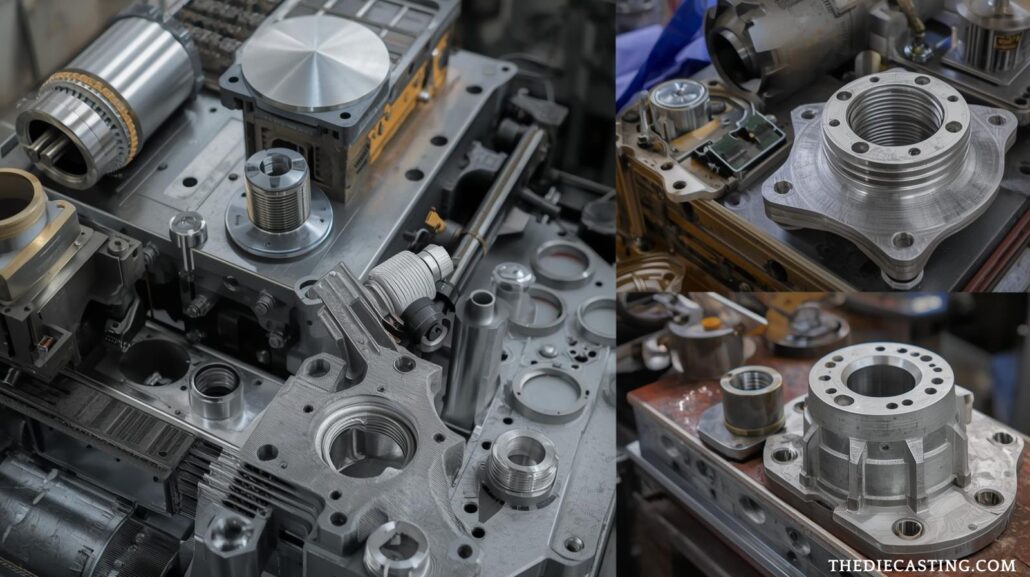

Besides heavy industries, the process is applied to consumer goods like power tools, kitchen appliances and energy elements like solar panel mounts and wind turbine connections. China’s cold chamber die casting machines are versatile, which is why they can manufacture durable and lightweight parts in large amounts to improve performance and design look in consumer and energy usage.
Benefits of Cold Chamber Die Casting
The cold chamber die casting process has several benefits that qualify it as a favourable technique of casting metal components of high quality and accuracy. These advantages make it very popular in various industries.
High Strength and Precision
This is done by means of facilitating manufacturers to make powerful, thick, and dimensionally precise elements. High pressure is used so that the molten metal fully fills the mould cavity without any gaps and/or voids. What is obtained is a solid part that has good structural integrity and uniform thickness. The right combination of these properties renders cold chamber die casting ideal with regard to parts that have to face mechanical loads or environmental stress, like automotive housings and structural components.
Applicable to High-melting alloys
The cold chamber process, as opposed to the hot chamber process, can deal with high-melting-point metals such as aluminium, magnesium, and copper. It is not possible to use these alloys in hot chamber machines because they corrode or are damaged by heat. The possibility of working with such alloys creates a chance to develop parts that cost less but are stronger and have high corrosion resistance – qualities that are necessary in the aerospace and automotive sectors.
Εξαιρετικό φινίρισμα επιφάνειας
Cold chamber die casting is the process which gives a smooth and detailed surface finish, leaving minimal or no secondary machining or polishing of the part. The end castings are clean and attractive with the right design of the die and proper cooling. The quality of the surface also enhances the performance of paint adhesion, coating, as well as sealing performance, and this saves time and cost in the post-processing stage.
Repetitiveness and Efficiency
After the die has been optimised and designed, it is possible to have the die reproduced thousands of times with little difference in the quality. This renders it ideal when it comes to the mass production of the same parts. With Chinacold chamber die casting machines, manufacturers can automate ladling, spraying, and ejection processes to improve the speed of production and lower labour costs without compromising the precision.
The Dimensional Accuracy and Complexity
Cold chamber die casting enables it to produce intricate geometries and thin-walled components that would otherwise be hard or impossible to produce using other processes. High-pressure injection of the metal is used, and this captures complex details of the die and provides tight dimensional tolerances. This accuracy minimises the machining requirement and ensures a perfect fit of the parts once they are fitted into bigger products.
Long Tool Life
Since the die is crafted out of hardened steel and it cools very well upon each firing cycle, it can survive thousands of fires before it requires replacement. This longevity lowers the tooling expenses in the long run, particularly when the production run is large in size.
Disadvantages and Limitations

Although cold chamber die casting has numerous benefits, it has its own shortcomings, which manufacturers should take into consideration before implementing it in a project. The knowledge of these limitations will assist in the selection of the appropriate casting process and in increasing production efficiency.
Slower Cycle Times
The cycle time is longer since the molten metal is ladled (by hand or semi-automatically) into the shot chamber, in an external furnace, and not by the hot chamber process. The other steps of handling and temperature control, which are performed in each cycle, slow down the speed of production a bit. Nonetheless, the current China cold chamber die casting machines that have built-in ladling systems have reduced this drawback to a minimal level.
Increased Setting Up and Tooling Costs
Initial costs of cold chamber die casting equipment and tooling are fairly expensive. Precision engineering is needed in dies, injection systems, and other auxiliary parts, and this adds upfront costs. But when the volume is high, the cost per part reduces significantly with time, and hence in the long term, the process becomes cost-effective.
Limited Alloy Range
Cold chamber machines are generally applied with high-melting alloys, including aluminium, magnesium, and copper. They cannot be used with low-melting metals such as zinc, lead or tin, which are normally done through the hot chamber method. This means that the choice of materials is slightly limited compared to other casting technologies.
Need for Skilled Operators
Due to the pressure control, temperature control, and time precision, the cold chamber die casting process requires skilled and highly skilled workers. Porosity, misruns, or cold shuts are some of the defects that can arise in the case of inconsistent ladling or improper injection pressure. To maintain consistent quality of products, training and supervision should be used.
Energy Maintenance and Consumption
A cold chamber system requires external furnaces and high-pressure hydraulic systems, both of which consume a lot of energy. It also requires regular maintenance to avoid any hydraulic leakage and die wear, as well as temperature imbalance. Failure to consider such aspects may impact productivity and product consistency.
Comparison of cold and hot chambers

Hot-chamber machines retain the melt in the machine and are quick. They fit well with low-melting alloys like zinc and lead. The furnace is separated by cold chamber machines. They are slower and can work with aluminium and alloys at high temperatures without corroding the machine. Select hot and zinc components. Pick cold alloy selection and bigger and heavier parts.
Economic aspects and size
Some of the major costs include tooling (dies), raw material, machine depreciation, labour, finishing, and quality check. The greatest initial cost is generally tooling. The cost per piece decreases rapidly with volume, and therefore, it needs economies of scale. In the purchase of machines, cheap machines save on capital but can cost more in scrap, need more maintenance or are not very automatable to save on the permanent labour costs. Consider the total cost of ownership and not the purchase price.
A Cold Chamber Die Casting Machine Components
A conventional china cold chamber die casting machine consists of:
- Frame/clamping unit: This is where high pressure is applied to the die.
- Injection system: Forces the molten metal into the die cavity at high velocity.
- Hydraulic system: Drives the movement of the plunger and die.
- Cooling system: Controls the temperature of dies.
The buying points to consider at a glance at suppliers of China cold chamber die casting machines.
- Request complete specifications: clamping force, volume of shot, stroke, and control system.
- Inquire about the use of automation: ladling/dosing, part handling and trimming stations.
- Check references and sample parts: Order photographs, x-rays and process sheets.
Take into account after-sales services and spares. In the case of Chinese machines, consider the lead time of parts and service. Numerous good Chinese manufacturers offer good prices and turnkey solutions – but service contracts count.
Cold Chamber Die Casting Trends of the Future
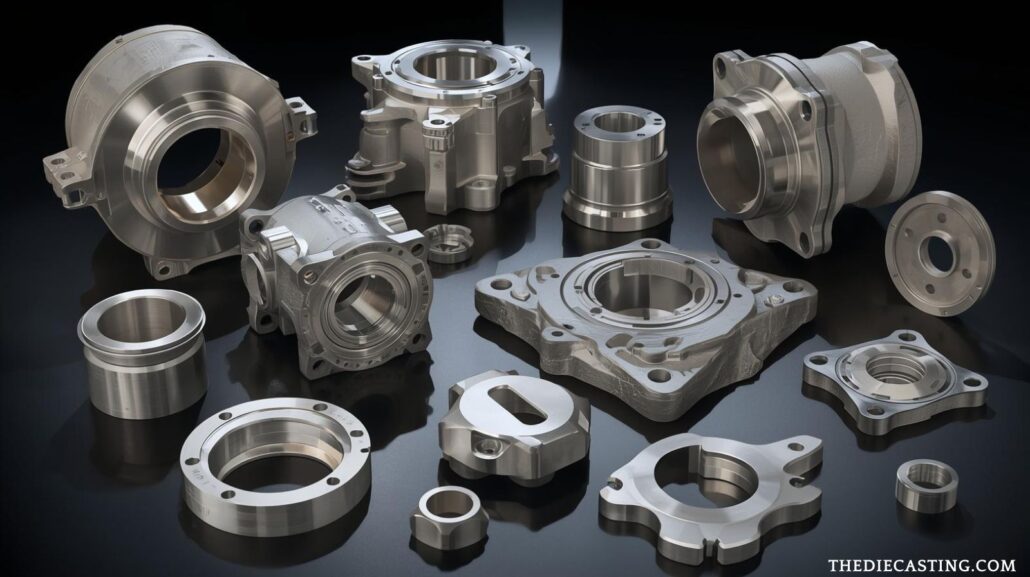

The cold chamber die casting process will keep on developing intelligent automation, AI control, and energy-efficient servo systems. Chinese companies are increasingly going to Industry 4.0 integration, which enables them to track production in real-time, foresee maintenance, and control quality using the cloud. There is also a trend towards lightweight materials such as magnesium alloys, where automotive companies are aiming at fuel efficiency.
The new hybrid systems are combining both vacuum die cast and cold chamber techniques in order to cut the porosity and enhance the surface integrity. The sophisticated sensors and injection control speed provide manufacturers with enhanced uniformity and less wastage.
Even more sustainable die casting lines with closed-loop cooling systems, automated alloy dosing, and virtual production with digital twins are going to be seen in the coming few years.
Τελικές σκέψεις
Cold chamber die casting has remained a pillar of present-day metal production. It is accurate, durable and efficient in the manufacturing of complex metal parts. In sourcing China, you should select a China cold chamber die casting machine that is affordable in terms of tonnage and control precision, and also provides long-term service coverage.
The buyer’s checklist can help you achieve an affordable solution without sacrificing quality by doing a comparative analysis of the models of machines. Investing in a dependable cold chamber set-up will provide the predictable results and profitability in the long run either case of producing automotive parts, structural housings, or electronic parts.









