Taottu alumiini on yksi luotetuimmista materiaaleista nykyaikaisessa suunnittelussa. Se muodostetaan puristamalla kiinteää alumiinia suurella määrällä lämpöä ja painetta. Se muuttaa metallin sisäistä rakennetta ja tekee siitä vahvemman ja sitkeämmän kuin valettu alumiini. Tämän vuoksi turvallisuutta ja kestävyyttä vaativat teollisuudenalat käyttävät taottua alumiinia. Alumiini itsessään on jo luokiteltu kevyeksi, korroosionkestäväksi ja monipuoliseksi. Sitä käytetään ajoneuvoissa, lentokoneissa, rakennuksissa, elektroniikassa ja jopa tavallisissa työkaluissa. Kaikki alumiinista valmistetut tuotteet eivät kuitenkaan ole samanlaisia. Metallin suorituskykyyn vaikuttaa suoraan se, miten metalli on muotoiltu.
Alumiini sulatetaan ja kaadetaan muotteihin, kun sitä valetaan. Tämä voi aiheuttaa virheitä, kuten ilmakuplia ja reikiä. Taonta poistaa nämä ongelmat. Sulattamisen sijasta alumiini puristetaan muotoon, jolloin raekoko pakotetaan mukautumaan osan muotoiluun. Näin saadaan erittäin voimakas ja homogeeninen materiaali.
Taottu alumiini on tullut suosituksi nyt, kun teollisuus on siirtymässä kevyempiin, turvallisempiin ja tehokkaampiin ratkaisuihin. Tässä artikkelissa kerrotaan, miksi se on parempi kuin valettu metalli, metallien takomiseen liittyvä prosessi, missä sitä käytetään ja alumiinin takomisen tulevaisuus.
Sisällysluettelo
ToggleMikä on taottu alumiini?

Taottu alumiini valmistetaan puristamalla kiinteää alumiinia korkeassa paineessa. Metallia ei sulateta kokonaan kuten valussa. Sitä pikemminkin kuumennetaan, kunnes se muuttuu pehmeäksi ja muokattavaksi. Pehmenemisen jälkeen alumiini leimataan tai hakataan haluttuun muotoon raskaiden taontakoneiden avulla. Tämä rasitus litistää metallia ja tekee myös sen sisäiset jyvät täydellisiksi. Rakeet suuntautuvat muodon suuntaisesti, ja ne parantavat osaltaan kappaleen lujuutta ja sitkeyttä. Näin hienojakoinen rakenne poistaa myös lukuisat valualumiinissa esiintyvät viat, kuten huokoset tai halkeamat. Näin ollen taottu alumiini on turvallisempaa, kestävämpää ja lujempaa.
Miten alumiini takomo toimii?

Taonta tehdään alumiinin takomossa. Prosessissa on muutamia vaiheita:
- Lämmitys - Alumiiniaihio kuumennetaan pehmeäksi, mutta ei sulavaksi.
- Muotoilu - Kuuma aihio asetetaan taontapuristimeen/vasaraan. Tarvittava muoto saadaan aikaan korkealla paineella.
- Jäähdytys - Taotun kappaleen annetaan jäähtyä hallitusti, jotta sen lujuus säilyy.
- Viimeistely - Lisätyöstö tai lämpökäsittely voidaan tehdä tarkkuuden lisäämiseksi.
Tämän prosessin tuloksena saadaan paksu, kiinteä ja homogeeninen osa. Siinä ei ole heikkoja kohtia tai ilmakuplia kuten valussa.
Taotun alumiinin edut
Valettu metalli ja muut materiaalit eivät pysty siihen, mihin taottu alumiini pystyy. Siitä on tullut ensisijainen työkalu teollisuudenaloilla, joilla ei ole varaa tinkiä suorituskyvystä ja turvallisuudesta.
Ylivoimainen lujuus
Taottu alumiini on erittäin vahvaa, ja tämä on yksi taotun alumiinin tärkeimmistä eduista. Metallin raerakenne jalostuu taontaprosessissa. Veto- ja väsymislujuus paranevat tämän linjauksen ansiosta. Väärennetyt komponentit kestävät raskaita kuormia sekä jännityksiä ja rasituksia toistuvasti ilman vikaantumista. Tämä asemoi ne myös erittäin hyvin korkean suorituskyvyn toiminnoissa, kuten lentokoneiden laskutelineissä, jousitusjärjestelmissä ja teollisuuskoneissa.
Kevyt mutta kestävä
Alumiini on luonnostaan kevyempää kuin teräs, ja taonta menee sen kanssa vielä syvemmälle. Taottu alumiini on erittäin vahvaa painoonsa nähden. Tämän ansiosta insinöörit voivat varmistaa, että he tekevät kevyempiä koneita ja ajoneuvoja, jotka ovat silti turvallisia ja vahvoja. Painonpudotus tekee autoista ja lentokoneista polttoainetaloudellisempia, mutta antaa niille myös kestävyyttä.
Lisääntynyt vastustuskyky väsymystä vastaan
Valetut osat kuluvat paljon enemmän kuin taottu alumiini. Väsyminen on tila, jossa osa on kulunut useiden rasitussyklien seurauksena. Heikon raerakenteen vuoksi valuosilla on taipumus halkeilla. Taottu alumiini ei halkeile helposti, joten tästä materiaalista valmistetut osat säilyvät pitkään niiden käyttäjien käsissä.
Yhtenäinen raerakenne
Taontaprosessia käytetään sovittamaan osan muoto metallin raekoon mukaan. Tällainen homogeeninen rakeisuus tekee iskusta entistä kovempaa. Päinvastoin, valaminen antaa mielivaltaisia raerakenteita, jotka luovat heikkoja kohtia.
Turvallisuus ja luotettavuus
Turvallisuus on etusijalla korkean paineen teollisuudessa, kuten ilmailu- ja avaruusteollisuudessa, autoteollisuudessa ja puolustusteollisuudessa. Taottu alumiini on luotettava, sillä se tarjoaa voimaa, kovuutta ja vakautta pitkällä aikavälillä, jopa äärimmäisissä olosuhteissa.
Alumiinin taonta käyttötarkoitukset
Alumiinin taonta on tehnyt vaikutuksen maailmassa, jossa tarvitaan painottomia, tehokkaita ja kestäviä osia. Taottujen alumiiniosien uskotaan olevan turvallisia, ja siksi niihin luotetaan yleisesti turvallisuuteen liittyvissä kriittisissä sovelluksissa.
Autoteollisuus
Nykyaikaiset autot ovat mukana vilpillisessä alumiinissa. Erittäin yleinen sovellus on pyörissä. Valettuihin pyöriin verrattuna taotut pyörät ovat kevyempiä, kestävämpiä ja turvallisempia. Tällainen painonpudotus parantaa ohjattavuutta ja polttoainetehokkuutta. Jousitusosat ovat toinen merkittävä käyttökohde, joiden on kestettävä raskaita kuormia, iskuja ja tärinää tiellä. Käytetty alumiini on taottua, joten ne eivät rasitu. Lisäksi useimmat moottorin osat, kuten yhdystangot ja männät, ovat taottuja. Nämä osat kestävät korkeaa painetta ja kuumia lämpötiloja pitkällä kestävyydellä. Lyhyesti sanottuna taottu alumiini parantaa auton suorituskykyä ja turvallisuutta.
Ilmailu- ja avaruusteollisuus
Lentokoneet vaativat komponentteja, jotka ovat luonteeltaan kevyitä ja vahvoja. Taottu alumiini sopii tähän eritelmään. Se koskee laskutelineitä, joiden on kestettävä suuria iskuja laskeutumisen ja nousun aikana. Sitä esiintyy myös siipirakenteissa, joissa tehokkuus riippuu keveydestä. Taotut alumiiniosat käsittelevät painetta, lämpöä ja tärinää lentokoneiden moottoreissa. Vikaantuminen ei ole vaihtoehto lennossa, ja siksi ilmailu- ja avaruusteollisuus luottaa takomiseen.
Armeija ja puolustus
Puolustussovellukset edellyttävät taottua alumiinia. Panssarivaunujen, lentokoneiden ja laivojen taottujen osien on kestettävä taistelujen äärimmäiset olosuhteet. Taonta takaa maksimaalisen sitkeyden, lujuuden ja luotettavuuden myös kaikkein vaativimmissa olosuhteissa.
Teollisuuskoneet
Suurlaitteita käytetään yleensä täydellä kuormituksella. Taotut alumiinituotteet ovat kulutusta kestäviä ja minimoivat seisokkiajan. Tämä tekee niistä kustannustehokkaita ja pitkäaikaisia ratkaisuja valmistajille.
Urheilu ja elämäntapa
Myös urheilu- ja lifestyle-tuotteissa käytetään taottua alumiinia. Taottuja komponentteja käytetään huippuluokan polkupyörien, kiipeilyvarusteiden ja urheiluvälineiden valmistukseen. Tällaisten esineiden on oltava kevyitä ja kestettävä pitkään, minkä vuoksi taonta on paras menetelmä.
Syy, miksi teollisuudenalat käyttävät taonta valun sijaan?
Taonta on teollisuuden valinta valun sijaan, koska se on luotettava ja turvallinen. Jäähdytysprosessin aikana valettuun alumiiniin muodostuu todennäköisesti vikoja. Huokoisuus, kutistuminen ja huono raerakenne muodostavat materiaaliin heikkoja kohtia. Tällaiset heikkoudet lisäävät mahdollisuutta, että valettu osa halkeaa tai murtuu jännityksen vuoksi.
Taottu alumiini ei sisällä näitä ongelmia. Taonta mahdollistaa metallin tiivistämisen, rakeiden hienontamisen ja metallin sisäosien poistamisen. Näin saadaan kovempi ja paksumpi kappale, joka kestää paremmin väsymistä. Esimerkiksi taotut pyörät voivat kestää hetkellisen iskun ja suuren painon rikkoutumatta, kun taas valetut pyörät voivat taipua tai rikkoutua, kun sama tapahtuu.
Erottelu on kirjaimellisesti elämän ja kuoleman kysymys kriittisillä aloilla, kuten ilmailu- ja avaruusalalla, autoteollisuudessa ja puolustuksessa. Sotilaslaitteet, jousitusvarret ja lentokoneiden laskutelineet eivät kestä äkillistä vikaa. Tämän vuoksi valmistajat suosivat takomista. Se tarjoaa voimaa, kovuutta ja luotettavuutta, joita ei löydy valusta.
Alumiinin taontaongelmat
Vaikka takominen tarjoaa paremman suorituskyvyn, siihen liittyy joitakin vaikeuksia. Näitä ovat korkeammat hinnat, suunnittelurajoitukset ja lisääntynyt tuotantoaika.
Korkeammat kustannukset
Taontaan tarvitaan työkalujärjestelmiä, raskaita puristimia ja uuneja. Nämä koneet ovat energiaa kuluttavia koneita, jotka tarvitsevat ammattitaitoisia käyttäjiä. Näin ollen takominen on kalliimpaa aloittaa kuin valaminen. Tämä voi olla haitta vähäarvoisille tai pienen budjetin tuotteille.
Monimutkaiset muodot
Valamisen etuna on se, että sulaa alumiinia voitaisiin myös valaa yksityiskohtaisiin muotoihin. Taonta puolestaan muodostaa kiinteää metallia paineen alaisena, mikä rajoittaa muotoilua. Nämä keksinnöt vähentävät jätettä, parantavat laatua ja tekevät enemmän kuin taottu alumiini.
Hitaampi tuotanto
Taonta ei ole yhtä nopeaa kuin valu. Jokainen osa on lämmitettävä, puristettava, jäähdytettävä ja jalostettava erikseen. Suursarjatuotantovalussa voidaan valmistaa useita osia samanaikaisesti, joten se on nopeampaa.
Miksi taonta voittaa yhä
Taottu alumiini on kuitenkin ensisijainen materiaali ilmailu- ja avaruusteollisuudessa, autoteollisuudessa, puolustusteollisuudessa ja raskaassa koneteollisuudessa. Näillä teollisuudenaloilla kustannuksilla tai nopeudella ei ole suurta merkitystä, vaan pikemminkin turvallisuudella ja kestävyydellä. Taottuun alumiiniin voidaan luottaa niin paljon, että lisäinvestoinnit ovat perusteltuja.
Kehitys alumiinin taonnassa
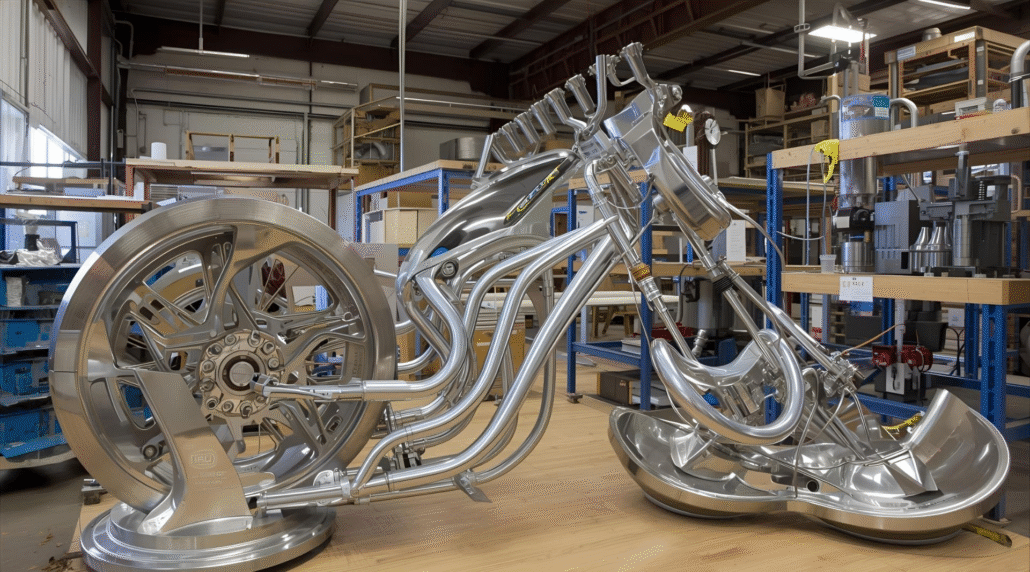
Nykyinen teknologia muuttaa alumiinin takomista tehokkaammaksi ja tarkemmaksi prosessiksi. CNC-työstö mahdollistaa mittojen ja pinnanlaadun tarkkuuden.
Tietokonesimulaatio
Rakeiden virtausta, jännityskohtia ja materiaalin käyttäytymistä voidaan nyt ennustaa simulointityökaluilla taonnan aikana. Tämä lujitusmenetelmä parantaa lujuutta, pintakäsittelyä ja kovuutta. Jätettä syntyy vähemmän, mikä säästää materiaalia ja kustannuksia.
CNC-työstön integrointi
Monet osat on vielä viimeisteltävä takomisen jälkeen. Taonta 3D-tulostetuilla alumiiniformuilla on yksi käytettävissä oleva innovaatio. 3D-tulostetut alumiiniset aihiot voidaan takoa, jotta niistä saadaan vahvempia ja tiheämpiä. CNC yhdistettynä takomiseen antaa valmistajille mahdollisuuden valmistaa monimutkaisia osia erittäin laadukkaasti ja tasalaatuisesti.
Hybriditaivutusmenetelmät
Toiset valmistajat eivät erota takomista eivätkä käytä muita valmistusmenetelmiä, kuten koneistusta tai lämpökäsittelyä. Teknologian kehittyessä alumiinin takominen on jatkossakin tärkeä osa autoissa, ilmailu- ja avaruusteollisuudessa sekä teollisuudessa. Se mahdollistaa myös sellaisten komponenttien valmistuksen, joilla on kapeat valmiudet huipputeknologiateollisuudessa.
3D-tulostus ja taonta
Tämä tekee taotusta alumiinista vaihtoehdon muille teollisuudenaloille, jotka haluavat vähentää hiilijalanjälkeä. Prosessin avulla voidaan valmistaa lähes verkkomaisia muotoja, jotka ovat kevyitä ja vahvoja.
Tulevaisuuden laajentaminen
Tämä kehitys alentaa tuotantokustannuksia ja tarjoaa uusia suunnitteluvaihtoehtoja.
Ympäristövaikutukset
Taottu alumiini on myös vihreää. Tässä on syy:
- Kestävyys - Mitä pidempään se kestää, sitä harvemmin sitä tarvitsee vaihtaa.
- Kierrätettävyys - Alumiinia voidaan kierrättää loputtomiin ilman, että se hajoaa.
- Energiansäästö - Kierrätysalumiinin takominen säästää energiaa verrattuna uuden materiaalin louhimiseen.
Ne ovat epäterveellisiä asioita, jotka heikentävät ja horjuttavat.
Taottu alumiini verrattuna muihin

Taottu alumiini vs. Valettu alumiini
Valettu alumiini on halvempi ja heikompi. Siinä on pieniä ilmakuplia ja jäähdytysvirheitä. Sen vuoksi alumiini on suositumpi näissä korkean rasituksen tilanteissa, ja magnesiumia käytetään itse asiassa merkittävästi siellä, missä sen päätarkoitus on vähentää painoa. Taottu alumiini on puristemuotoista. Rae liikkuu muodon mukaan, mikä tekee siitä kovemman ja painavamman. Taottu alumiini on aina ylivoimainen turvallisuuskriittisissä komponenteissa.
Taottu alumiini vs. teräs
Teräs on tehokkaampaa kuin alumiini, ja se on paljon raskaampaa. Tämä suurempi paino laskee auton ja koneen polttoainetehokkuutta. Taottu alumiini on kuitenkin edelleen suosittua sen hinta-lujuus-kestävyys-suhteen vuoksi. Se ei voi koskaan vastata terästä puhtaassa lujuudessa, mutta se tarjoaa paljon sitkeyttä murto-osalla painosta. Siksi ilmailu- ja avaruusteollisuus sekä autoteollisuus käyttävät yleensä taottua alumiinia teräksen sijasta.
Taottu alumiini vs. titaani
Titaani on erittäin sitkeä ja syövyttämätön metalli. Se on kuitenkin myös kallista ja vaikeampaa käsitellä. Taottu alumiini on edullisempi ja helposti muotoiltavissa. Alumiini ei täysin korvaa titaania, mutta ilmailu- ja avaruusalalla sekä puolustusteollisuudessa sen käyttö rajoittuu osiin, joissa tarvitaan lujuutta mutta ei paljon massaa, ja siksi se on parempi korvata alumiinilla.
Taottu alumiini vs. magnesium
Magnesium on halvempaa kuin alumiini, mutta se ei ole yhtä vahvaa. Se syöpyy helposti, ja sen väsymiskestävyys on heikko. Alumiini voidaan takoa, jolloin se tarjoaa enemmän lujuutta ja käyttöikää. Valmistuksesta voidaan tehdä voimakkaampi ja ominaispiirteellisempi kuin valualumiinista, joka sisältää virheitä, kuten huokoisuutta ja epätasaisuutta raerakenteessa.
Taottu alumiini vs. hiilikuitu
Hiilikuitu on erittäin kevyttä ja erittäin tehokasta. Sen valmistus on kuitenkin erittäin kallista ja sitä on vaikea korjata. Taottu alumiini on halvempaa, yksinkertaisempaa työstää ja se voidaan kierrättää. Hiilikuitu on valittu suorituskyvyn perusteella tietyillä teollisuudenaloilla. Alumiinin kevyt lujuus ja pitkäikäisyys vauhdittavat alumiinin takomista pitkälle tulevaisuuteen.
Alumiinin takomisen tulevaisuus
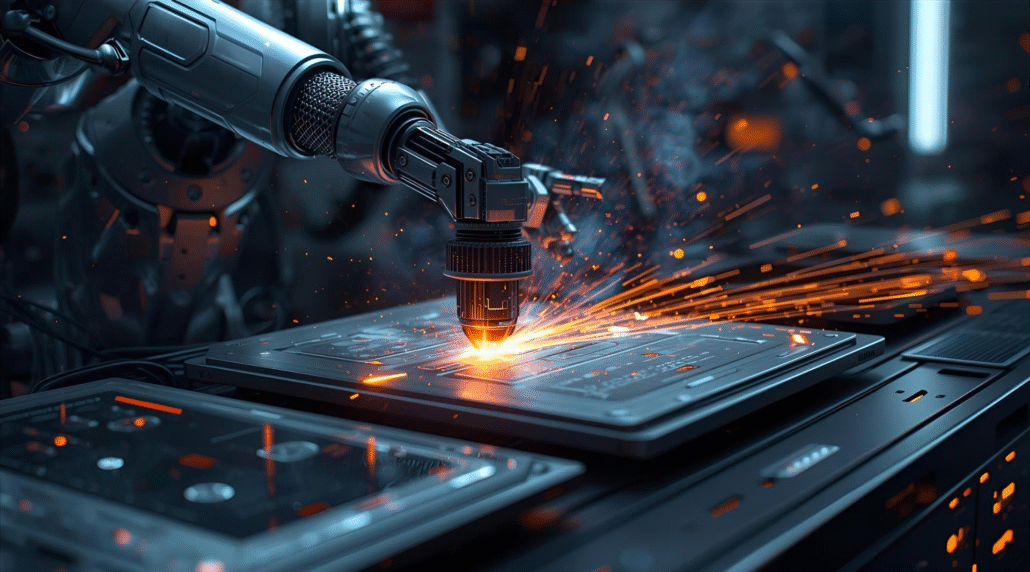
Taonnan ja 3D-tulostuksen yhdistelmä on tarjonnut uusia mahdollisuuksia ja mahdollistanut kevyempien ja vahvempien mallien valmistamisen. Tähän kysyntään vaikuttavat useat suuntaukset eri puolilla maailmaa.
Ensimmäinen syy on siirtyminen sähköajoneuvoihin vaikuttavalla vauhdilla. Sähköautoissa tarvitaan komponentteja, joilla ajoneuvon kokonaispaino pidetään alhaisena ilman, että se vaikuttaa sen turvallisuuteen. Siihen vastaa taottu alumiini, joka voi tarjota korkean lujuus-painosuhteen. Taonta on prosessi, jossa rakeiden virtaus sovitetaan osan muotoon hallitun lämmön ja paineen avulla, jotta voidaan muodostaa osia, jotka kestävät suurta painoa, toistuvaa rasitusta ja epäsuotuisia olosuhteita. Taotut osat, kuten pyörät ja jousitusvarat sekä akkukotelot, ovat entistä tärkeämmässä asemassa, kun sähköautojen käyttö lisääntyy.
Myös ilmailu- ja avaruusteollisuus on kasvanut. Lentoyhtiöt tilaavat yhä enemmän lentokoneita vastatakseen kasvavaan matkustajamäärään, ja puolustusohjelmat edellyttävät, että lentokoneet ovat kehittyneitä hävittäjiä ja lennokkeja. Taottu alumiini on avainasemassa tässä teollisuudessa, sillä laskutelineiden, siipirakenteiden ja moottorin osien on oltava erittäin kestäviä mutta erittäin kevyitä.
Toinen kysyntäkerros on sotilas- ja puolustusmenojen lisäys. Nykyaikaisessa maailmassa valmistetut panssarivaunut, panssaroidut ajoneuvot, laivat ja lentokoneet vaativat materiaaleja, jotka kestävät äärimmäisiä taisteluolosuhteita. Taottu alumiini tarjoaa tällaisissa olosuhteissa vaadittavaa vakautta ja lujuutta.
Päätelmä
Taottu alumiini on yksi nykyaikaisen valmistusmaailman luotettavimmista komponenteista. Siksi taottua alumiinia tulisi käyttää niillä teollisuudenaloilla, joilla turvallisuus ja suorituskyky ovat tärkeimpiä. Taottujen pyörien, jousitusjärjestelmien, moottorin osien jne. autoteollisuuden sovelluksiin kuuluu komponentteja, jotka parantavat polttoaineenkulutusta ja kuljettajien vakautta.
Se muodostaa tulevaisuuden suunnittelun ja innovoinnin perustan, sillä mikään ei ole tehokkaampaa, turvallisempaa ja kestävämpää. 3D-tulostuksen ja takomisen yhdistelmä on tarjonnut uusia mahdollisuuksia, ja nyt voimme valmistaa kevyempiä ja tehokkaampia malleja. Ilmailu- ja avaruusteollisuudessa käytettävien taottujen laskutelineiden, siipirakenteiden ja turbiinin osien odotetaan kestävän äärimmäisiä voimia. Puolustusala on toinen teollisuudenala, jolla tarvitaan taottua alumiinia panssarivaunuissa, lentokoneissa ja merivoimien järjestelmissä, eikä vikaantuminen ole vaihtoehto.
Taonta on nykyisin kalliimpaa ja vie enemmän aikaa kuin valu, mutta tekniikan kehittyminen, kuten tietokonesimulaatiot, CNC-työstö ja hybridivalmistus, on tehostamassa menettelyä. Se on seuraavan sukupolven tekniikan ja innovaatioiden perusta, sillä mikään ei vedä vertoja sen tehon, turvallisuuden ja kestävyyden yhdistelmälle. Taottu alumiini on jatkossakin tärkeä hyödyke, kun teollisuudenalat muuttuvat kaikkialla maailmassa. Syy siihen, miksi insinöörityöllä ja innovaatiolla on lupaava tulevaisuus, on se, että lujuutta, turvallisuutta ja kestävyyttä ei voi rinnastaa.










