Principaux fournisseurs d'aluminium moulé sous pression en Chine et dans le monde
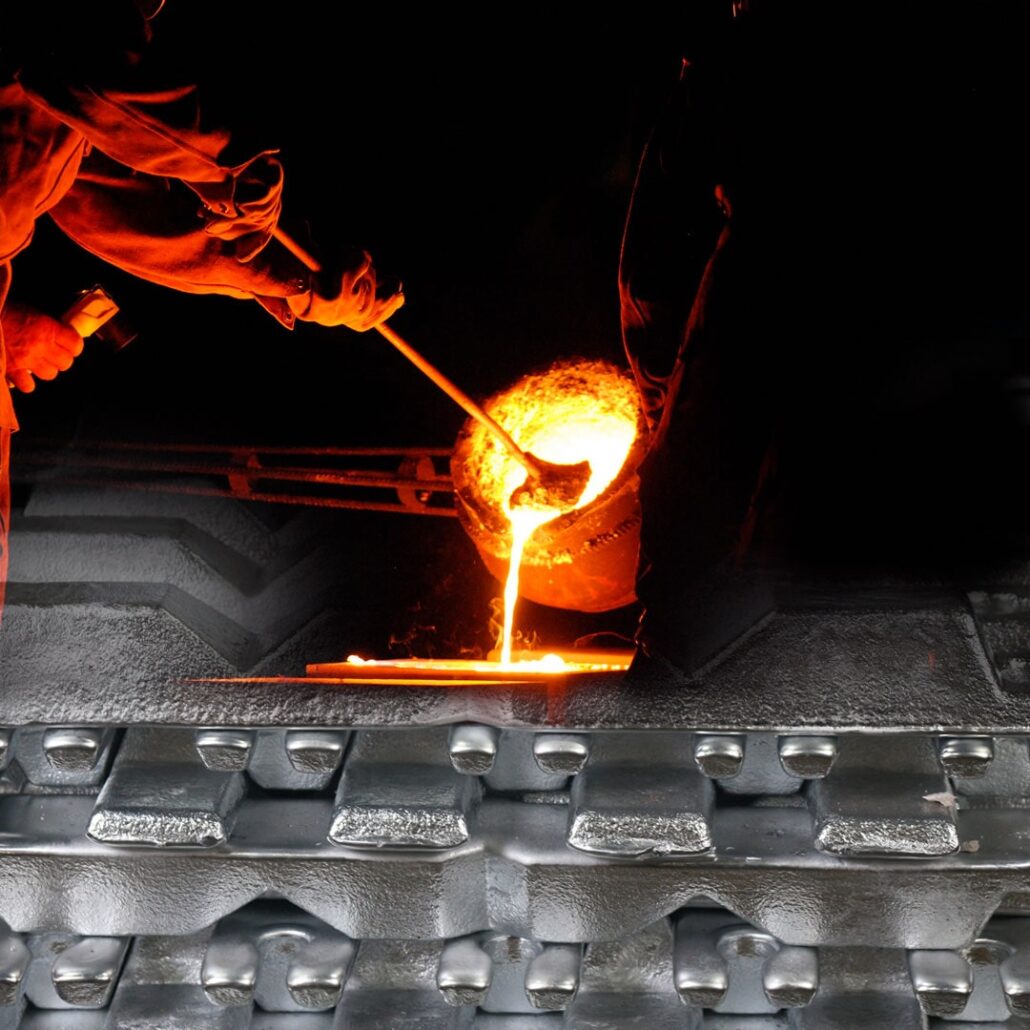
fonte d'aluminiumThe precise metal component market experiences rapid growth globally across aerospace technology sectors and industry, including automobile, electronics and medical devices and industrial machinery. Advanced metal parts produced industrially for low-weight applications require the high-pressure die casting method. The superior position among die casting techniques belongs to aluminium since it merges durable performance with weight reduction potential while protecting against corrosion, as well as efficient heat transfer capabilities and the flexibility to shape designs. Organisations pursue efficient manufacturing by choosing experienced die casting suppliers based at locations all across the world. Businesses make their supplier selection choices based on an assessment of engineering competence, combined with quality controls and operational growth capacity and material management capabilities and tooling speed and delivery. The conditions serve as fundamental factors to preserve industry compliance while maintaining consistent, large-scale product outputs. Suppliers emerge as the best options depending on their advanced CNC machinery, as well as their mould development and surface finishing capabilities. Aluminium die casting operations in China bring together people from around the world to maintain low manufacturing costs and a consistent supply system. Performance. The aluminium die casting suppliers Sincere Tech and GC Precision Mould, and CNM Tech have established themselves through impressive manufacturing innovation and industry accreditations, which they match with personalised customer service. Global businesses can access die casting mould suppliers who deliver equal usability through U.S., European, Indian and Mexican operations, which include manufacturers who optimize technology advancement to achieve premium-quality standards. The following article analyses China-based suppliers alongside international suppliers of die casting services. The companies on this list received thorough evaluation based on operational characteristics while also considering their track record of successful projects plus client feedback about quality aluminum die casting and tool development services. What is Aluminium Die Casting? Molten aluminium experiences high-pressure injection into a die mould during aluminium die casting to create precise aluminium components. The production method serves multiple manufacturing sectors because it creates durable metal components with complex shapes and delivers superior finish quality. The production of metal parts through aluminium die casting attracts major demand from automotive and aerospace industries, alongside consumer electronics manufacturers, because of its important advantages. The processing begins with aluminium melting in a furnace until liquefaction, then dies into a steel mould by the force of a die-casting machine. The aluminium solidifies inside the mould when it cools down, since the mould contains a precise representation of the part design. The operator removes the part through the mould opening after casting is complete. Manufacturers achieve parts with complex and precise geometries through this technique, which they cannot create with conventional manufacturing tools. HPDC and low-pressure die casting represent the two principal forms within the die-casting process. HPDC requires high-speed pressures between 1,500 and 20,000 psi to inject molten metal into the mold which generates fine surface details and products with smooth finishing. For producing large-scale products experts employ low-pressure die casting technology because it delivers the metal at reduced pressure thus producing less defective outcomes. Advantages of Aluminium Die Casting The primary reason for aluminium preference as a die casting material is the combined qualities of light weight and a superior strength-to-weight ratio because of the qualities of aluminium to produce items that will have to be durable and light alike. Its good thermal and electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and ease of machining also make aluminium popular in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Additionally, die-cast aluminium parts are recognised for their exact dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finish, where often their need renders secondary processing in the way of machining unnecessary, saving time and costs. Other than the high-pressure injection method, it also guarantees that all of the components have the same thickness, which reduces the possibility of having weak spots or flaws in the finished part. Applications of Aluminium Die Casting The automotive industry shapes components such as engine blocks and transmission casings, as well as cylinder heads, by using aluminium die casting technology. The aerospace industry employs aluminium die casting for producing lightweight, strong components, which serve to improve product strength, together with lowered fuel usage and safety levels. The process finds great favour in the production of electronic housings as well as heat sinks and a variety of complex elements that require exceptional reliability and strength. Aluminum die casting operates as a flexible production technique that enables the construction of complex intricate products with superior quality characteristics. For achieving durable components and precise product specifications manufacturers must utilize pointed-aluminum from its molten state. The requirement emerges from business demands for top performance quality parts. Sincere Tech Year of Establishment: 2005No. of Employees: 100–500Business Type: Plastic injection mould manufacturing, aluminium die casting, CNC machining, and assembly. Website and Contact: Website: plasticmold.netEmail: info@plasticmold.netPhone: +86 135 30801277Address: Building 1, No. 30 Huan Zhen Rd, Shang Dong village, Qi Shi Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong, China, 523000 Company Profile Sincere Tech is one of China’s top manufacturers of development of plastic moulds, aluminium die casting, high precision CNC machining, and full assembly. Located in Dongguan City, Guangdong Province of China, the company has between 100 and 500 skilled professionals with the capability of providing complete product development solutions from initial concept to final product. Based on a client-centric approach and cutting-edge equipment, Sincere Tech provides precision turning of die-cast aluminium parts to satisfy the stringent requirements of the automotive, electronics, medical and consumer products industries. On top of being an established die casting mould supplier, the company provides added value to customers, with services like surface finishing, prototyping, as well as quality testing. For North America, Europe and Southeast Asia, the clients have relied on sincere tech to build long-term partnerships on top aluminium die casting suppliers. Their Quality Commitments Through the entire manufacturing process, the sincere tech is committed to satisfactory quality without compromise. The company follows international standards such as ISO 9001 and ensures its quality methods, such as in-process inspection, mould flow analysis, and final dimensional validation. Sincere Tech guarantees that