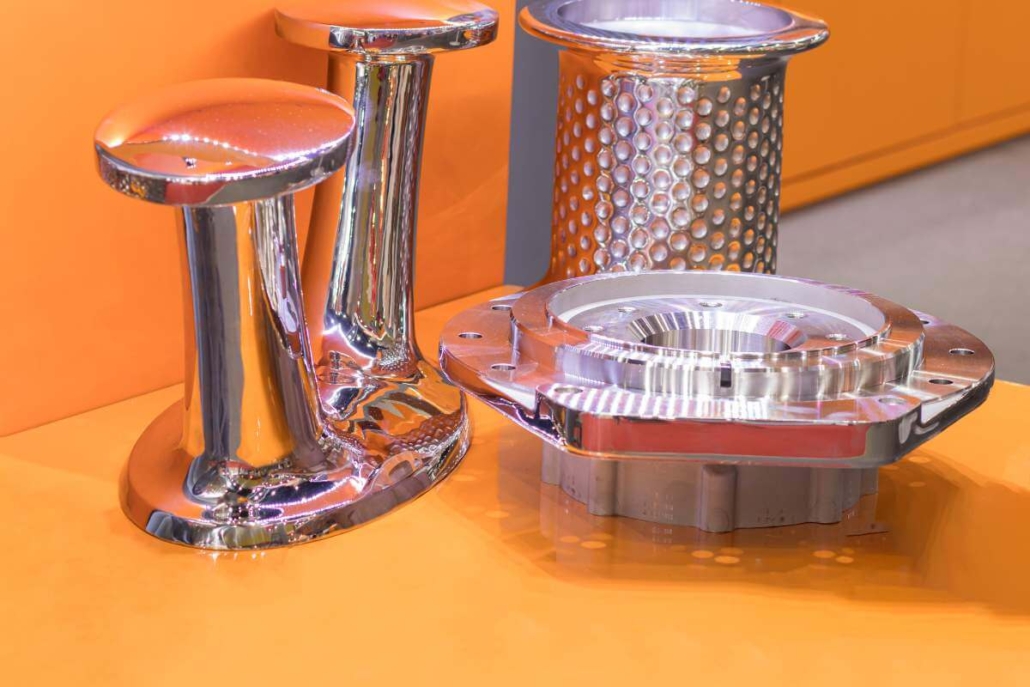
ザマックとは?ザマックとは何か?
ザマック5, ザマック2 ダイカスト, ザマック3, ザマック 3 ダイカスト, ザマック3亜鉛鋳造Alloys contribute significantly to the development of delicate electronic parts as well as heavy parts used in vehicles. For example, zamak metal has quietly changed the way many industries operate. This metal is renowned because it is strong, can be molded easily and is versatile. The word Zamak originates from German and stands for zinc, aluminum, magnesium and copper. During the early years of the 20th century, the production of brass alloys aimed to improve on the brittleness found in previous zinc-based products. Today, zamak is used widely in vehicle, electronic device, and hardware manufacturing. It is appreciated both for its sturdy structure and for finishing smoothly with only a little work. Producing aluminum requires less energy than other materials since it melts easily, and it is also attractive because it can be recycled. Each different grade of zamak fits various needs, such as zamak 3 being softer than zamak 5, which is stronger than zamak 12. Most household goods and industrial products made with zamak metal meet the rising needs of manufacturing because they are practical and of good quality. Here, we will explain what zamak metal is made from, types such as zamak 3, zamak 5, and zamak 12, its functions, plus the positives and negatives. Zamak is a type of zinc alloy Zamak is made from zinc, mixed with a small amount of aluminum, magnesium, and copper. The word Zamak stands for Zink, Aluminum, Magnesium, and Kupfer, which are the German names for the metals involved. Due to its high-quality casting and appearance, zamak metal is popular in manufacturing automotive, electronic, furniture, and consumer goods. The process called die casting allows Zamak metal to shape complex, strong, and cost-efficient parts. Bending zamak into steel forms shaped like the finished goods is done at high pressure, producing many complex shapes very rapidly while needing only a minimal amount of machining. Because its melting temperature (around 385°C) is lower, zinc is more efficiently shaped than metals such as steel or aluminum in a foundry. What is Zamak, and how is it made? Zamak is a name formed from the German words for the main metals: Zink (zinc), Aluminium (aluminum), Magnesium, and Kupfer (copper). In the 1920s, the New Jersey Zinc Company created zamak to help overcome brittleness that affected some zinc alloys. It is viewed as a high-quality type of zinc that gives better die casting than most other materials. The usual elements in zamak metal are 96% zinc, 4% aluminum, a little bit of magnesium and some copper. As a result of this mix, its metal product is very strong, lasts a long time and can be formed into exact shapes with high precision. Key points about Zamak Metal A highlight of zamak metal is that it is very easy to cast. Manufacturers can create shapes with thin walls out of aluminum that would usually be pricey or difficult to produce using other materials. In addition, zamak has a polished surface, which makes it suitable for use in parts that need painting or plating. One more advantage is that steel retains its shape. Because Zamak does not change shape easily, it is commonly used in car and electronics manufacturing. The material is strong relative to its weight, making it attractive. Unlike aluminum, zamak does not weigh very little, but it offers a good level of durability that makes it useful for items that must be manageable. Uses of Zamak Metal Because it has great mechanical characteristics, zamak metal is applied in many products. In this industry, stainless steel is found in door handles, mirrors and several interior parts. A variety of electronic parts use Zamak because it is both precise and can resist heat. The furniture sector uses zamak because it is so versatile, fitting into hinges, brackets, and other decorations. Many fancy pieces in fashion include zamak since it is shiny and does not get tarnished easily. The process of making Zamak metal by casting 1. Alloy Preparation To produce zamak metal, you need to combine zinc, aluminum, magnesium and copper in the right ratios. To extract metals from these ones, the raw materials are melted at moderate temperatures. The right ratios are necessary to ensure that zamak 3, zamak 5 and zamak 12 provide the desired qualities. 2. Melting The blend of materials is put into a furnace and brought up to the zamak melting point of 385°C (725°F). During this step, the alloy flows very well and is therefore excellent for high-pressure die casting. 3. Die Casting The zamak is melted and then put into a die casting machine to be injected into a metal mold. Thanks to this process, items are shaped into very detailed and sturdy forms. Depending on how the casting will be used, manufacturers select from products classified as zamak 3, zamak 5, or zamak 12, since each is meant for a different purpose. 4. Injection and Outflow As soon as the zamak is injected, cooling the mold causes the metal to harden fast. After removing the part from the mold, it may not need machining because the alloy has a clean finish. 5. Finished and Plated When the model is cast, it might be polished, painted, or electroplated in materials such as nickel or chrome. The processes improve the look and resilience to corrosion of the manufactured product, mostly when used outside. Applications of Zamak Metal Zamak metal is used in several industries because of its superior casting, its strong properties and attractive smoothness. Even in the automotive industry, zamak metal plays a key role by being useful and attractive. 1. Automotive Industry Many door handles, emblems, mirror housings and interior details in motor vehicles are manufactured using zamak metal. Because it can be designed intricately and held to small measurements, it’s useful in parts that are either noticeable or not. The reason Zamak 5 is used most often here is that it is more durable and wears less easily. 2. Consumer Electronics Its stable dimensions and smooth appearance