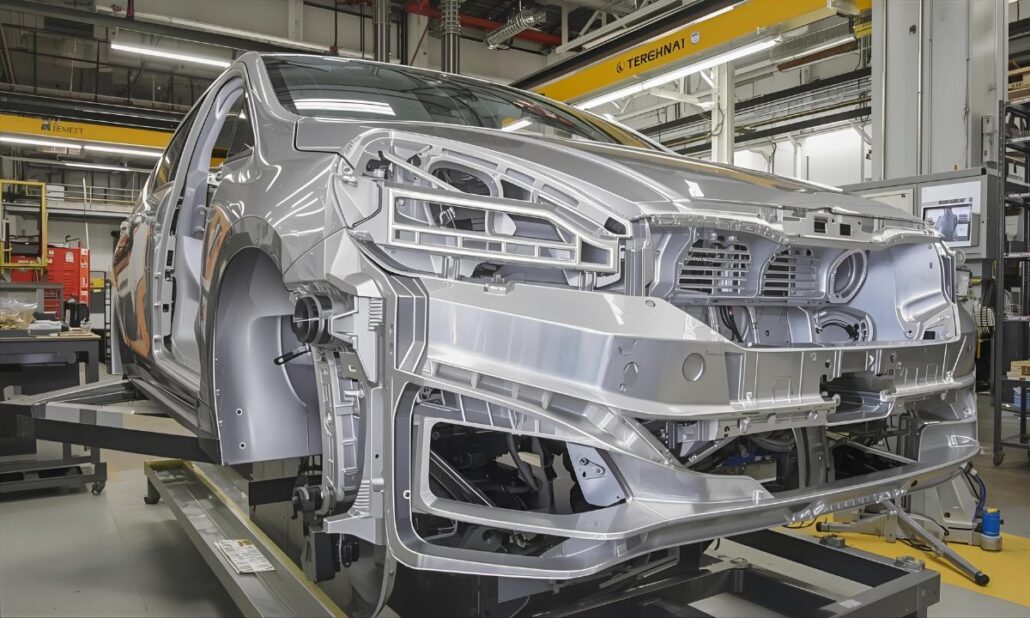

Aluminium automotive die casting in China has become an essential process within the international automotive supply chain that contributes to efficiency, sustainability, and innovation in vehicle production. Lightweight and strong, aluminium provides a special balance between mechanical performance and fuel consumption, which contemporary car manufacturers require. Through minimised vehicle weight, aluminium die-cast components have a direct impact on reducing fuel consumption, longer battery range in electric vehicles (EVs), and carbon emissions. This not only renders the technology significant to the manufacturers, but also to environmental regulations across the world.
This domination in the automotive industry of China is a natural extension of aluminium die casting. Being the largest producer, the country with huge production rates, with its large supply chain and the support of the government through industrial policy, China has already established itself as the largest producer and one of the greatest innovators in the area. The die casting sector of the country serves both local car manufacturing industries and foreign brands, and it provides engine blocks and transmission housings, as well as high-tech giga castings, applied to the body of EVs.
The development of lightweight materials and more environmentally friendly production technologies has become even faster. This congruence between industrial competency and the world sustainability targets will keep China on the frontline of the technology of aluminium die casting, which is the future of automotive engineering.
What is Die Casting of Aluminium?
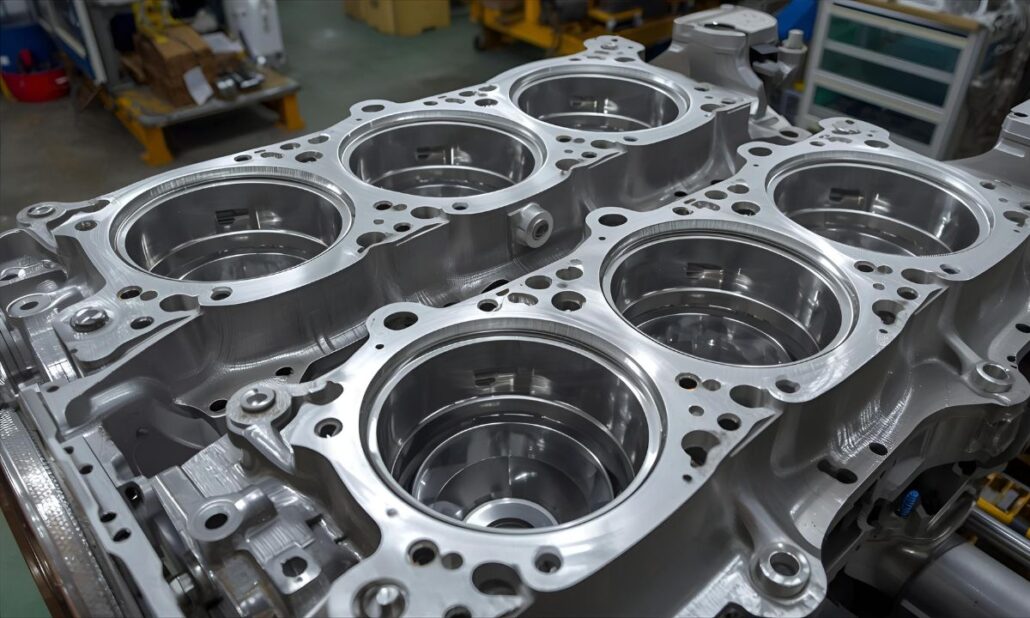

Aluminium die casting is the production technique where molten aluminium is pressurized and injected into a high-pressure steel mold (die). Upon cooling and solidification, the metal produces complex and precise components with very favourable strength-to-weight ratios. The automotive parts that are commonly manufactured are engine blocks, transmission housings, wheels, brackets, and structural body parts.
Why China Leads in Aluminium Die Casting?
- Scale of manufacturing – China has thousands of die-casting firms, small suppliers, and multinational joint venture die-casting firms.
- Cost Advantage – The labour costs and wide supply chain are competitive, making production economical.
- Technological Advancements – Most of the Chinese manufacturers have embraced high-pressure die casting (HPDC), vacuum die casting, and semi-solid casting in an effort to produce better quality products and fewer defective products.
- Government Provisions – The policies that promote lightweight vehicles and electric mobility have increased the demand for the aluminium cast parts.
Aluminium Die Casting Process
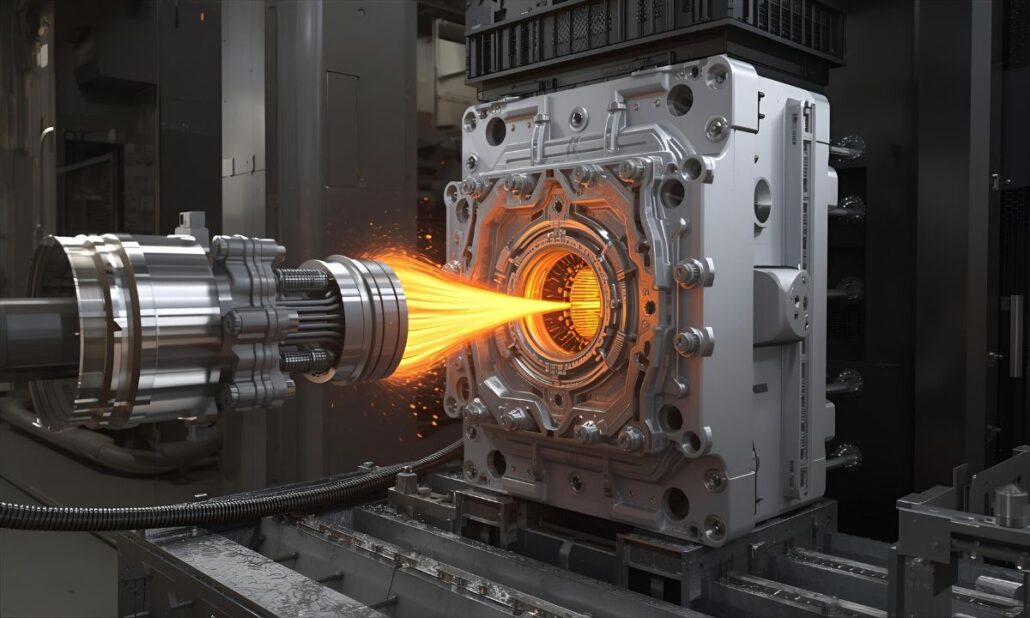
Aluminium die casting is one of the most specialized manufacturing techniques that allows the creation of complex and accurate automotive components with great mechanical properties. It does include several well-regulated phases, and each of them can be seen as a step toward the quality, strength, and durability of a final product. The following is a discussion of each of the stages:
1. 금형 준비
The steel mold, usually of hardened tool steel, is completely cleaned and checked before production starts and should be free of wear or damage. Then the release agent or lubricant is applied to the cavity of the mold, which has a variety of significant purposes. It avoids the sticking of the molten aluminium to the die, provides smooth part ejection and assists in maintaining mold temperature in successive casting cycles. It is important to prepare the mold properly, as this has a direct relation to the surface quality and dimensional accuracy of the finished component.
2. Melting & Alloy Preparation
It begins with the melting of aluminium ingots or recycled scrap in a high-temperature furnace that can be either gas-powered, electrically powered or induced. At this phase, molten aluminium is observed keenly to maintain an optimal temperature range of around 660 to 700 °C to provide a fluid mass and reduce defects. Elements like silicon, magnesium, and copper are alloyed in order to improve certain properties such as strength, corrosion resistance, or thermal conductivity. It is important to keep the chemical composition accurate since a slight change in it might greatly affect the functionality of automotive elements.
3. High-Pressure Die Casting (injection)
After the molten aluminium attains the desired state, it is poured into the prepared steel casting mould by a high-pressure die casting (HPDC) machine. The pressure of injection is usually between 110 and 175 MPa, and this makes the liquid metal fill even in the most complex molding cavities with accuracy. High pressure also aids in reducing porosity and shrinkage flaws to produce high-strength and dense parts. This is regarded as the centre point of the process since it determines the quality of the casting and whether complicated shapes can be produced without breaking the structural integrity.
4. Cooling & Solidification
The molten aluminium is then injected and quickly cools down and hardens in the steel mould. The rate of cooling is maintained throughout to make sure that the crystallization is uniform and internal stresses or warping are minimized. Cooling time varies greatly with the thickness and intricacy of the component being cast; a thin-walled component could be solidified in a matter of seconds, whereas a more complex part could take a longer cycle to solidify. Well-organised cooling circuits (water channels or oil circuits built into the die) are commonplace with the aim of ensuring consistency throughout the production runs. It is essential to attain a balance of strength, ductility, and dimensional accuracy by proper solidification.
5. 배출
After the part has hardened, ejector pins in the mold force the casting out. In this step, accuracy is needed to prevent burning sensitive areas or thin walls of the part. Large-scale automotive manufacturing often relies on automated ejection systems, which guarantee the consistency of cycle times and minimize manual work. The process of ejection may appear to be easy, yet with improper application, it might cause surface defects, cracks or misalignment, which will adversely affect the usability of the final product.
6. Trimming & Finishing
Raw casting may contain large quantities of extraneous material, such as flash, runners or even gates, after ejection, and this needs to be removed. A hydraulic press or a CNC machine is usually used in trimming to attain an accurate edge line. Other finishing processes like shot blasting enhance the texture of the surface, and machining provides the high dimensional tolerance needed by engine or transmission components. They can be heat-treated to increase strength and hardness, and coating or anodizing may increase corrosion resistance. These are the necessary secondary processes because through them the raw casting is taken to the next level, where it is turned into a functional and reliable automotive component.
7. Inspection & Quality Control
The last step is the intensive inspection, whereby all castings will be of automotive quality. Dimensional checks are inspected with the help of coordinate measuring machines (CMM), porosity and internal flaws are revealed with the help of X-ray inspection or non-destructive testing (NDT) means like ultrasonic scans. Surface finish and mechanical strength are also put through tests to determine adherence to specifications. Statistical process control (SPC) and modern electronic monitoring systems may also be introduced in large-scale production to ensure the quality of thousands of materials is consistent. Considering the importance of these parts to both vehicle safety and its performance, these parts need tight quality control.
Sourcing Materials to use in Automotive Aluminium Die Casting

In China, automotive die casting mainly utilises alloys of aluminium which are selected due to their weight strength ratio, corrosion and recyclability.
Common Aluminium Alloys
ADC12 (Al-Si-Cu alloy)
- Large automotive parts are commonly used in China because of their high castability and corrosion resistance.
- Uses: Engine block, gearbox housings, structural parts.
A380
- Good strength, thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Uses: Transmission housings, brackets and heat management systems.
AlSi9Cu3
- Thin-walled components can be used with high fluidity and pressure tightness.
- Uses: (In engines) Engine covers, cylinder heads.
AlSi10Mg
- Good heat-treated mechanical properties.
- Uses: EV structural components of safety significance.
Key Material Considerations
- Impurity Control: The amount of iron must be on a small scale to prevent brittleness.
- Recyclability: Secondary (recycled) aluminium is broadly applied to save money and energy.
- Performance Requirement: Alloys are selected according to mechanical requirements (tensile strength, fatigue resistance, thermal conductivity).
- Surface Treatment Compatibility: Materials must be compatible with anodizing, powder coating, or plating for corrosion resistance.
Applications in the Automotive Sector
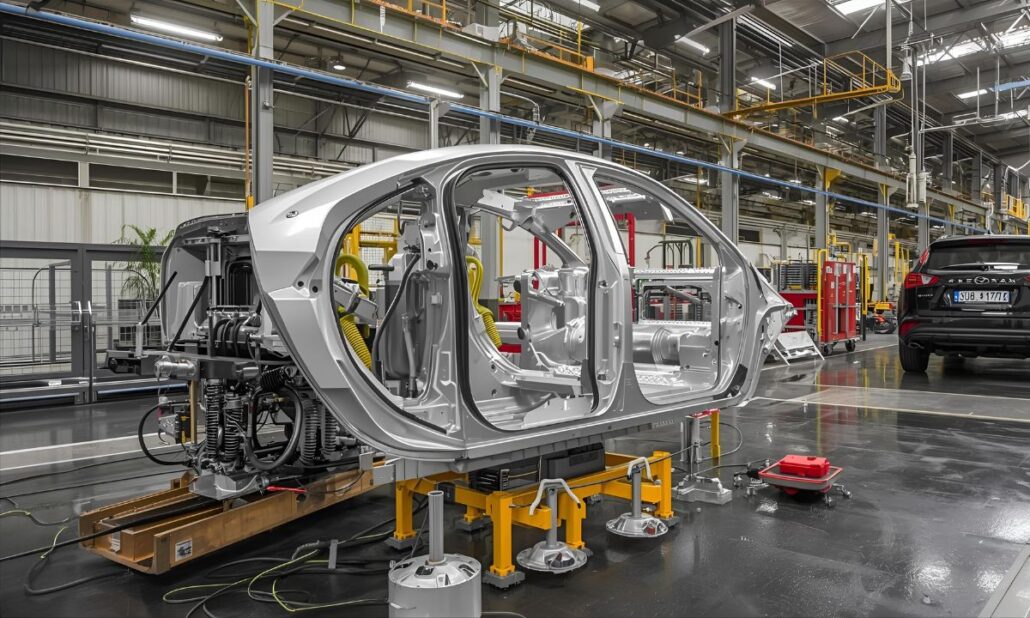

Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Lightweight aluminium die-cast components are now invaluable in the electric vehicle sector, where overall vehicle weight reduction is directly proportional to the energy efficiency and range of the vehicle. Battery housings, motor enclosures, and large body-in-white components are all becoming more and more manufactured by high-pressure die casting. Aluminium usage not only maximize safety due to its structural integrity, but will enable car manufacturers to optimise thermal performance of batteries, as it is essential to performance and life cycles. Die casting is a fundamental technology of the rapid shift to clean mobility nationwide in China, where EV manufacturing is the leader of its category globally.
Engine & Transmission
Aluminium die casting is commonly applied to make housings, cylinder heads and gearbox casings in traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. All these parts have to endure high temperatures, vibrations, and mechanical stress, which is why the weight-to-strength ratio of aluminium is a strong point. With the substitution of the heavier cast iron with aluminium, automakers can get significant changes in the total mass of the vehicle without compromising on the longevity. This will help achieve improved fuel economy and a reduction of emissions. Chinese die casters are also providing the hybrid vehicle producers with lighter, but high-performance engine and transmission parts to fill the gap between traditional and electric mobility.
Structural Parts
There is a growing replacement of multiple-welded or bolted steel assemblies with large aluminium die-cast components. This change makes assembling a vehicle simpler, minimizes the number of parts and increases structural rigidity. The impact energy-absorbing characteristics of Aluminium make it of special interest to crash-relevant applications like shock towers, subframes and cross-members. To manufacture complete rear or front bodies of the vehicle in a single piece of aluminium, some Chinese manufacturers are using giga casting technology. This enhances not only crashworthiness but also lowers the cost of production and assembly, and is in line with the global trend of creating light, safe and efficient cars.
Heat Management Systems
The thermal conductivity of aluminium is better, and it is therefore the preferred material for management systems within a conventional vehicle and an electric vehicle. Radiators, intercooler housings and battery enclosures are dependent on an aluminium die casting to provide adequate thermal regulation. In the case of EVs, the optimal battery temperatures are important in performance, charging rate, and safety. With die-cast aluminium housings, automakers can produce a compromise between lightweight design and high thermal performance. Chinese manufacturers are also making heavy investments in precision die casting to fulfil the rising demand for high-end thermal management solutions in the fast-growing EV market.
Challenges and Trends

Quality Standards
Strict international quality certification, such as IATF 16949 and ISO 9001, is a prerequisite for suppliers who want to compete in the world automotive markets. These standards apply to all levels of production, from the sourcing of raw materials to the final inspection, and this makes parts reliable and uniform. In the case of Chinese die casting firms, these standards are not only a prerequisite to be able to export to Europe and North America, but also a path to gain trust among local automobile manufacturers. High-level inspection technologies, statistical process control, and automated quality monitoring are gaining wide usage to fulfil such challenging requirements.
Environmental Pressure
Aluminium die casting process is very energy-consuming, especially in smelting and melting. As the environment has become more concerned and government regulations have become tougher, manufacturers in China are under more pressure to be greener. They are introducing energy-efficient furnaces, waste heat recovery, and integration of renewable power in order to reduce carbon emissions. Further, the push to meet the targets of carbon peak by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060, as proposed in China’s targets known as the dual carbon, has increased the rate at which sustainable casting technologies are being invested in. Those companies that do not adapt might not be competitive enough because global automakers pay more attention to the environmentally responsible supply chain.
Innovation Drive
With the introduction of Tesla Giga Casting, the auto die casting industry has been redefined because it proved that a car can be cast in a single large block, and an entire vehicle can be produced. The innovation lowers the number of parts, assembly and the cost of production, as well as enhancing the rigidity of the vehicles. Chinese firms are not left behind, and they are investing in ultra-large high-pressure die casting equipment with over 10,000-tonne clamping forces. Companies like LK Group and Yizumi are currently designing and marketing these machines, which place China at the head of the world mega casting competition. This tendency is a transition between traditional component casting and mass, structural-level manufacturing innovation.
Sustainability
One of the most significant trends in aluminium die casting is sustainability. Recycling aluminium is economically attractive and also consumes less energy, up to 95 per cent of primary aluminium production. The recycling capacities of Chinese manufacturers are also increasing fast, so as to have a constant supply of secondary aluminium to use in die casting. Car manufacturers are also collaborating more with suppliers of casting to achieve closed-loop recycling, whereby the manufacturing scrap is collected and remelted back into use. Not only does this move to a circular economy reduce costs, but it also assists businesses to cut down their carbon footprint, satisfying not only their regulatory requirements, but also the demands of customers for a more environmentally-friendly car.
Market Size and Growth
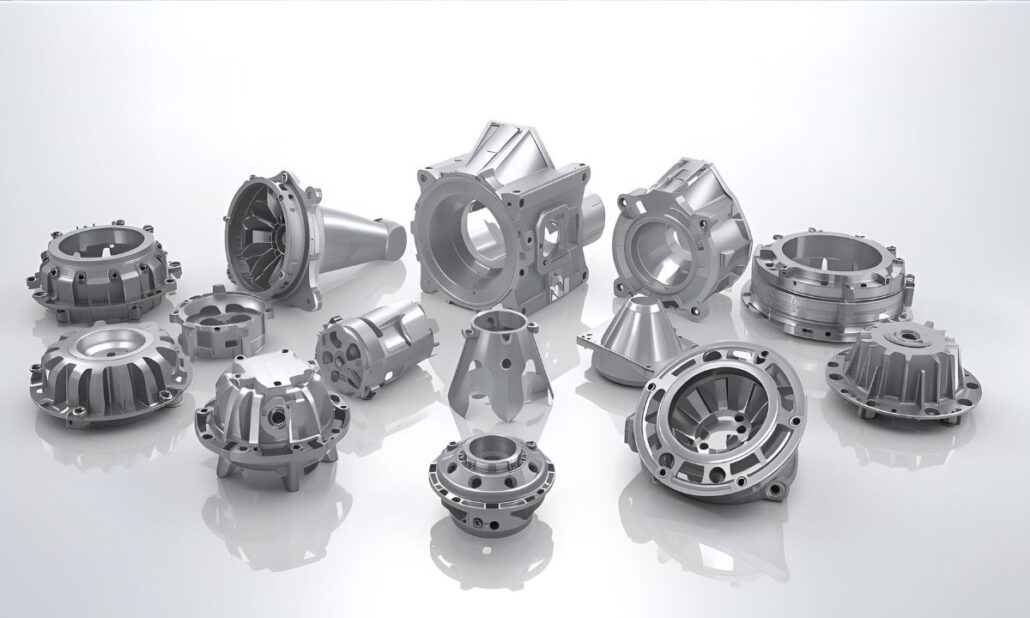

China contributes over 50 per cent of all the aluminium die casting manufacturing in the world, thus it is the largest manufacturing regional powerhouse. It is projected by the industry that the Chinese aluminium die casting market would reach USD 25 billion and grow by 7-9 per cent/year by 2030. Increasing electric vehicle production, the accelerating need for lightweight automotive solutions in order to comply with fuel and emission regulations, and the proliferation of Chinese automakers worldwide are the drivers of this growth.
Key Manufacturing Regions in China
Some of the provinces dominate in automotive aluminium die casting. Guangdong Province has emerged as a very large hub that deals with automotive and electronic die casting with a strong export network. Zhejiang Province is the region that has made a name in terms of precision casting and has close relations with foreign car manufacturers. Shandong and Jiangsu, in the meantime, have concentrations of large units of high-capacity foundries serving not only local manufacturers but also the foreign markets, which becomes even stronger because China is the leading world producer of die casting.
| 합금 | 주요 속성 | 일반적인 애플리케이션 | Notes on Use in China |
| ADC12 | Excellent castability, good corrosion resistance | Engine blocks, gearbox housings, brackets | Most widely used alloy in China for automotive casting |
| A380 | High strength, good thermal conductivity | Transmission housings, engine covers, heat exchangers | Popular for both domestic and export markets |
| AlSi9Cu3 | High fluidity, good pressure tightness | Cylinder heads, thin-walled parts | Suitable for complex shapes and precision parts |
| AlSi10Mg | Strong mechanical properties, heat-treatable | Structural EV components, crash-relevant parts | Increasingly used in giga casting and EV applications |
| Secondary Aluminium | Lower cost, sustainable, energy-efficient | General automotive components, non-critical parts | Widely adopted to support recycling and carbon goals |
Technology Innovations
Chinese die casting firms are adopting new technology in an effort to remain competitive:
- Giga Casting: To follow Tesla, some companies like LK Group and Yizumi are making 10,000+ ton die casting units of large body-in-white (BIW) components.
- Vaccum Die Casting: Pores within the aluminium pieces are minimised, and the metals are then used in safety-related parts of the automobile.
- Automation & Robotics: Robotic arms used to spray, extract and trim to enhance regularity and optimization.
- 시뮬레이션 소프트웨어: This is the Advanced mold flow analysis that will aid in minimizing defects before production.
Role in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing
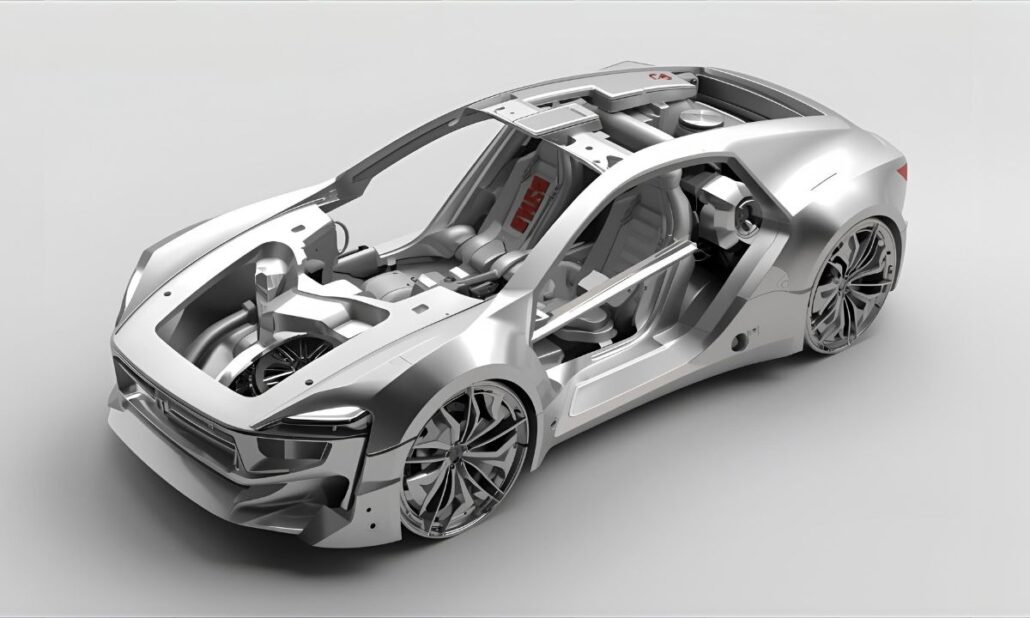

The electric car market is a primary growth area in China in the aluminium die casting industry. Die-cast aluminium is common in battery casings, motor casings, and chassis, and it enhances thermal performance, strength, and efficiency. Aluminium facilitates a long driving range and cost reduction by decreasing the weight and number of parts of any vehicle. As China manufactures more than 60 per cent of the EVs in the world, demand is still growing.
Sustainability/ Recycling
Most die casting of aluminium in China has become more sustainable, with recycled aluminium taking over centre stage. It consumes only a quarter of the energy needed to produce primary smelting and reduces the costs and emissions. Smelters are becoming more and more partners of automakers to facilitate circular economy models. Following the principles of the Chinese targets of the carbon dual, recycling and cleaner processes offer long-term benefits to manufacturers who want to achieve competitiveness and international confidence.
Competitive Landscape
The aluminium die casting industry in China is quite competitive, and major players operate in the sector, providing the domestic and international markets. Ningbo Tuopu Group specializes in supplying structural parts to international automakers, and Dynacast has precision plants in China. Guangdong Hongtu Technology specialises in EV battery components, whereas Wencan Group specializes in lightweight parts for European automobiles. The companies underscore the rising leadership of China in the field of advanced die casting.
향후 전망
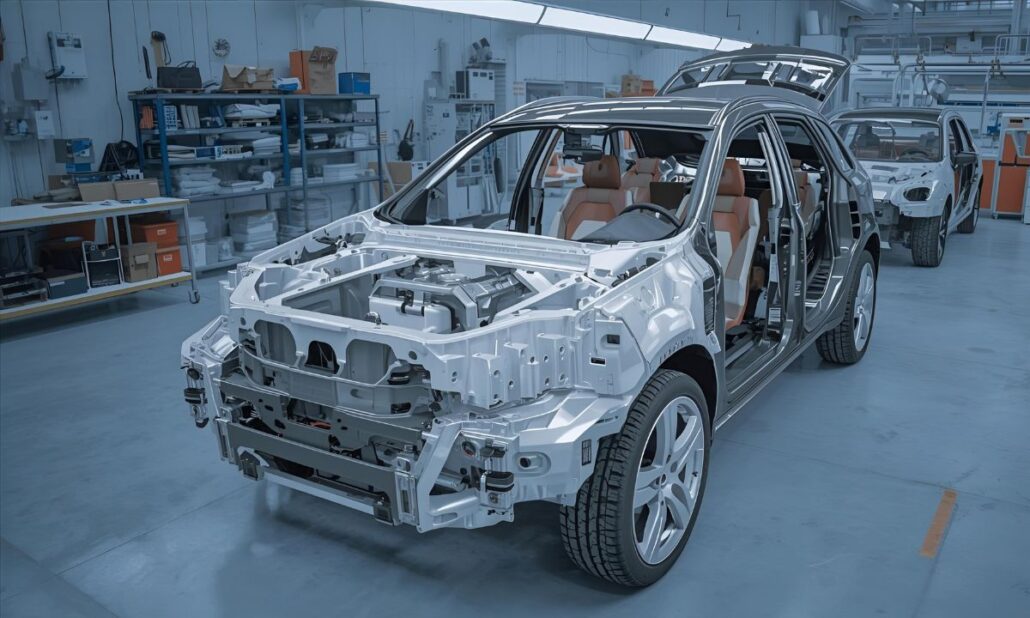

Technology and international changes in the automotive industries will have a strong connection with the future of aluminium automotive die casting in China. Among the biggest changes is the adoption of the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and smart manufacturing in casting processes. Through AI-based predictive maintenance, defect detection and real-time monitoring, manufacturers will be able to minimize downtime, enhance quality, and maximize efficiency, which makes production more predictable and cost-efficient.
The other trend is the growth of the Chinese die casting firms into international supply networks. There is a trend of many firms stepping out of domestic markets to turn into Tier-1 suppliers to major original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in Europe and North America. This is indicative of the increasing technical capability of Chinese suppliers and the rising dependence of the world automakers on the competitive Chinese production capacity.
The industry is also taking a new shape due to the move towards mega casting. Following the concept of giga casting developed by Tesla, the Chinese manufacturers are investing in ultra-large high-pressure die casting machines that can cast parts of vehicle underbodies in one piece. The innovation has produced a reduction in the complexity of assembly, an increase in structural integrity and low production costs, which makes it very desirable in future vehicle platforms, particularly electric vehicles.
Finally, sustainability leadership is becoming a marker of long-term competitiveness. The companies, which would practice recycling technologies, use secondary aluminium and invest in low-emission methods of smelting, will benefit economically and environmentally. With China on its path to achieving carbon neutrality, die casting companies that fit the agenda will be in a better position to comply with the regulations, meet the international market demands, and drive the industry into a green future.
결론
그리고 automotive die casting industry of aluminium in China is at the stage of its high growth, influenced by the world demand to find a lightweight, efficient and environmentally friendly transportation mode. With automakers moving toward the production of electric vehicles, the demand for aluminium-based products or battery enclosures, motor housings, and structural parts is likewise speeding up. This trend underlines the significance of die casting technology in minimizing the weight of the vehicle, enhancing efficiency, and complying with strict environmental rules. Chinese manufacturers are also investing in modern processes, including high-pressure die casting, vacuum die casting and giga casting, thus remaining competitive on an international basis. Simultaneously, a gradual transition toward recycled aluminium and green production makes the industry consistent with national levels of carbon reduction. China is consolidating its role as the largest automotive manufacturer in the world, as well as a technology leader in the global alumnium die casting.
