Aluminium-Druckgießereien in den USA
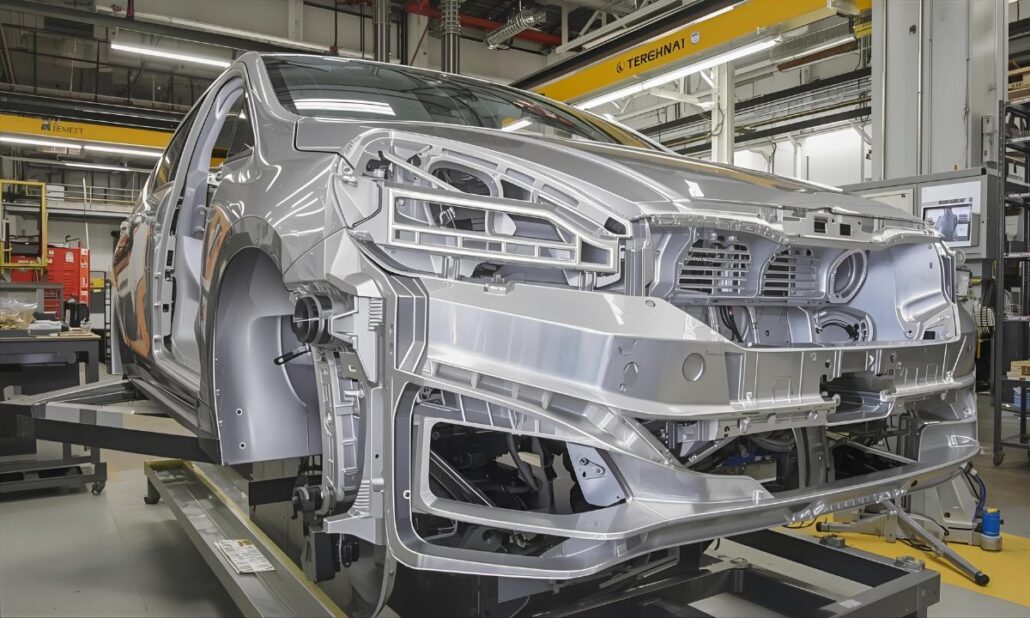
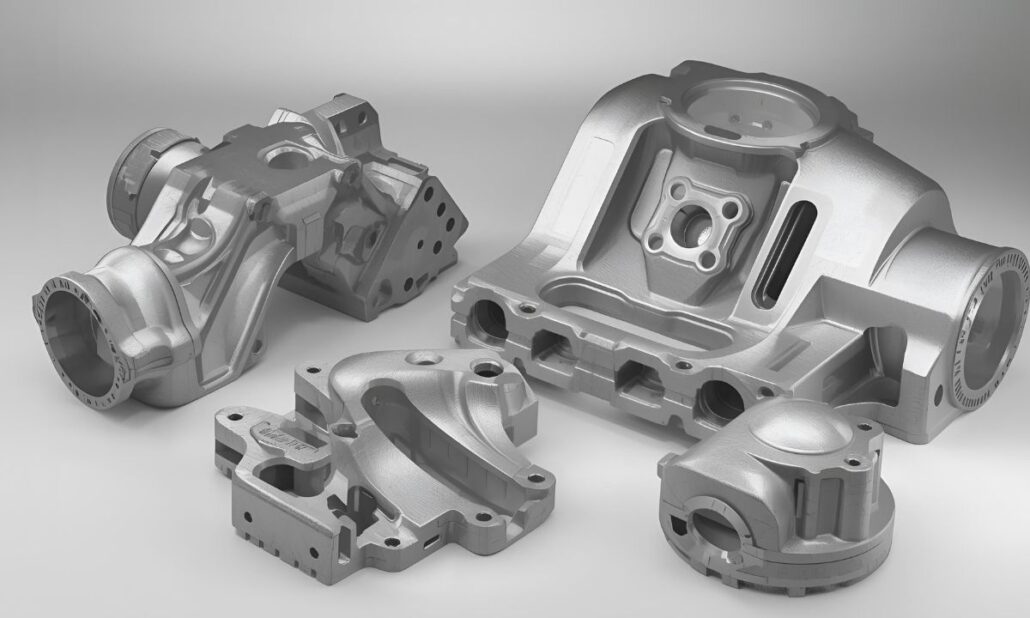
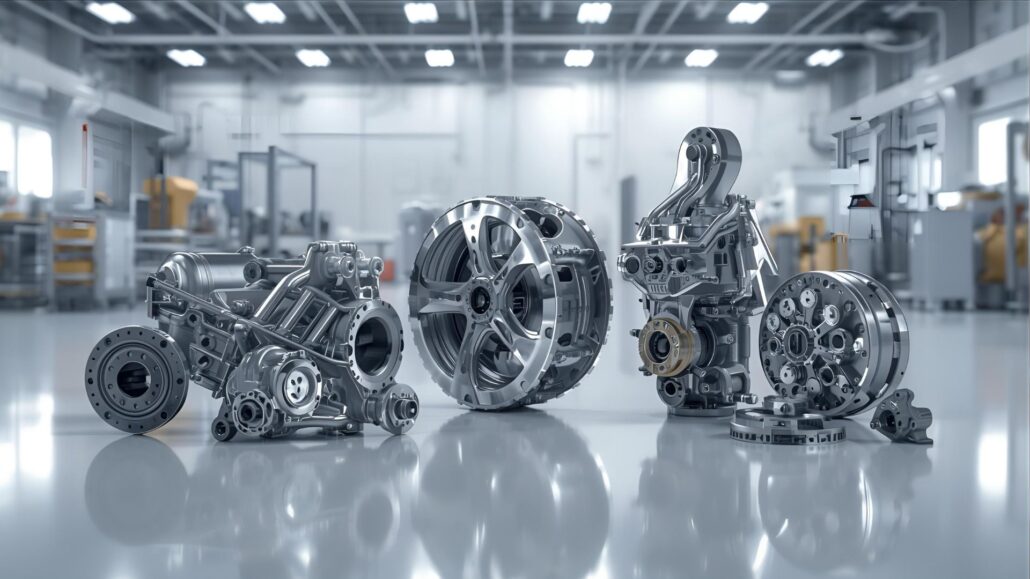
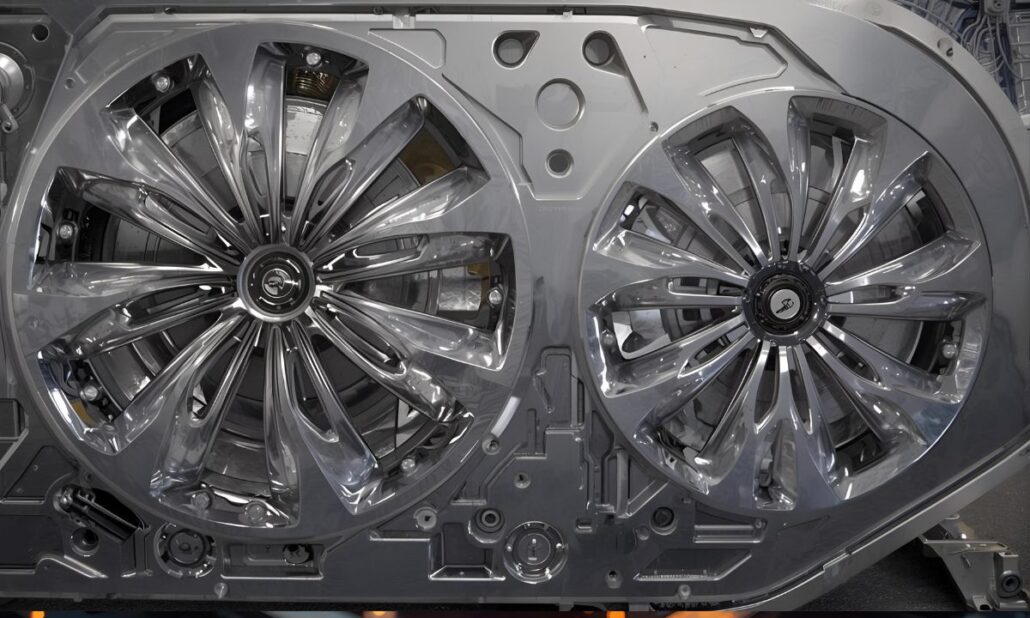
Aluminiumdruckguss, Druckgussunternehmen, DruckgussunternehmenAluminum die casting is now one of the surest and most economical production procedures in the United States of America, particularly to manufacturers that require robustness, longevity and precision. This is done by high pressure injection of molten aluminum into steel castings and this produces parts which are not only lightweight but also dimensionally accurate and durable. It is this strength and low weight that makes aluminum die casting the material of choice in the automotive and aerospace industry, electronics, industrial machineries, and consumer goods. The U.S market boasts of some of the most established aluminum die casting industry worldwide in the form of large scale manufacturers with global presence to small and specialized firms, specializing in custom parts and niche applications. These firms are very crucial in the sustenance of the key industry by supplying such segments of the industry as engine blocks, transmission housings, electronic enclosures, and structural parts. The U.S. based manufacturers have earned their reputation of reliability and innovative products in the world through their high quality technologies, certification and focus on quality products. The trend in the last few years has seen a massive surge in demand of die-cast aluminum parts because of the recent developments in lightweighting of vehicles, the production of electric vehicles, and the drive to manufacture energy efficiently. American firms are embracing automation, sustainable castings, and superior alloys so as to achieve high results to meet these requirements. This article lists some of the best aluminum die casting manufacturers in the USA and their achievements, potential, and contributions to the contemporary industry. It does not matter whether you are getting parts to perform a large-scale manufacturing process or a highly-technical application, these manufacturers are the embodiment of the finest American technology in aluminum die casting. What Is Aluminum Die Casting? Aluminum die casting is a production technique where high pressure on a molten aluminum is forced into a steel mold also referred to as a die. When the metal cools and solidifies the mold is opened and the completed part is ejected. This is the process with the help of which the manufacturers can create strong, light and highly detailed components with high level of dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes. The fact that aluminum die casting can produce complex shapes that would otherwise be challenging or costly to produce using other manufacturing processes is the key benefit. It finds extensive application in the manufacture of such parts as engine blocks, transmission housings, electronic enclosures, heat sinks and structural components. The Aluminum Die Casting has several major advantages: Thanks to such strengths, aluminum die casting has emerged as a better alternative in industries, which require dependable and efficient components of high-quality to match its technical and economical necessities. Top USA Aluminum Die Casting Companies 1. Dynacast International Dynacast International has been one of the best known companies in the area of precision die casting globally. The company has decades of experience in the production of small, complex components with the use of aluminum, zinc and magnesium alloys. They are good at producing components that have stringent tolerances and that have complex features, which are needed by the automotive, consumer electronics, telecommunications, and medical devices industries. Being global also means that Dynacast is able to serve small businesses and multinational companies with the flexibility, innovations and quality that do not vary among projects. 2. Pace Industries Having become the largest die casting companies in North America, Pace industries have established a good reputation of offering to offer solutions in totality. Their service ranges include designs and engineering support, die castings, machining, surface finishing and final assembly; they have been providing a one-stop solution to clients in the automotive, industrial and consumer industries. High-volume projects and custom projects can be dealt with because of the scale of their operations. Pace also follows the culture of putting money in the modern technology and sustainable practices such that they can be able to remain competitive in the rapidly changing industry. 3. Ryobi Die Casting (USA), Inc. Ryobi is a renowned brand in the world die casting segment, and it has a major presence in the United States. Their operations in the U.S. are centered on medium to large scale aluminum die cast components, majorly to the automotive sector. Ryobi manufactures engine block, transmission housing, and structural parts that they need to be durable and precise. The firm has utilized cutting edge technology and quality management which has seen it become a supplier of choice to major automobile manufacturers in the world. 4. Gibbs Die Casting Gibbs Die Casting, the other leader in the U.S. market is based in Henderson, Kentucky. The company specializes in the aluminum and magnesium die castings in the automotive industry, especially the transmission housings and power train parts. Gibbs lays strong emphasis on innovation where automation and sophisticated manufacturing techniques are being used to ensure high standards of efficiency and quality of work. The company also incorporates the concept of sustainability in its business by curbing wastage and encouraging environmental friendliness business practices. 5. Apex Aluminum Die Casting Co., inc. Apex Aluminum Die Casting is situated in Ohio and it is used in automotive, electronic, and appliances industries. The business is reputable in working with mid-volume production lots, which makes it the perfect option with firms that require a steady output quality but does not require the enormous powers of bigger importers. The team of Apex is concerned with customer satisfaction, reliability of service, engineering and accuracy in manufacturing. They have established themselves as a reliable partner to a number of U.S. companies because of their good reputation to deliver consistent results. 6. KenWalt Die Casting Company KenWalt Die Casting is based in California and has over several decades of experience with producing die castings; aluminum and zinc. The firm also focuses on bespoke jobs and serves the industries of both industrial equipment and consumer goods. KenWalt stands out as a company that collaborates closely with the client during the