Prezentare generală a industriei companiilor de turnare sub presiune a zincului
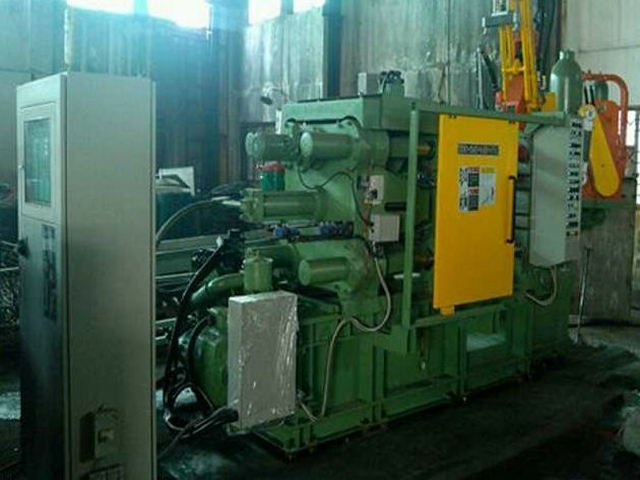
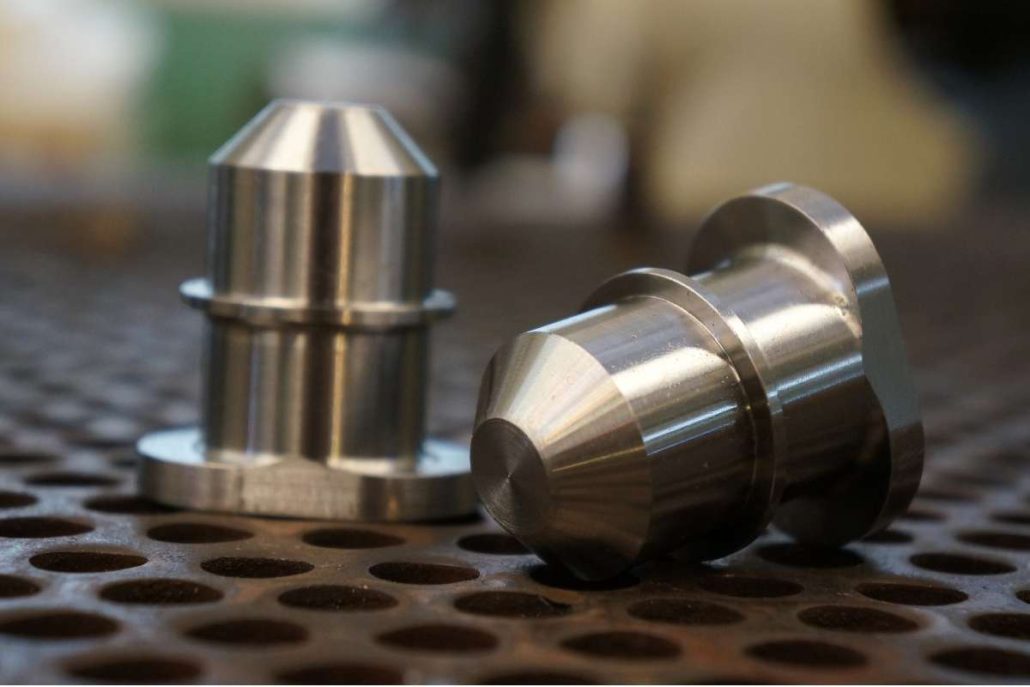
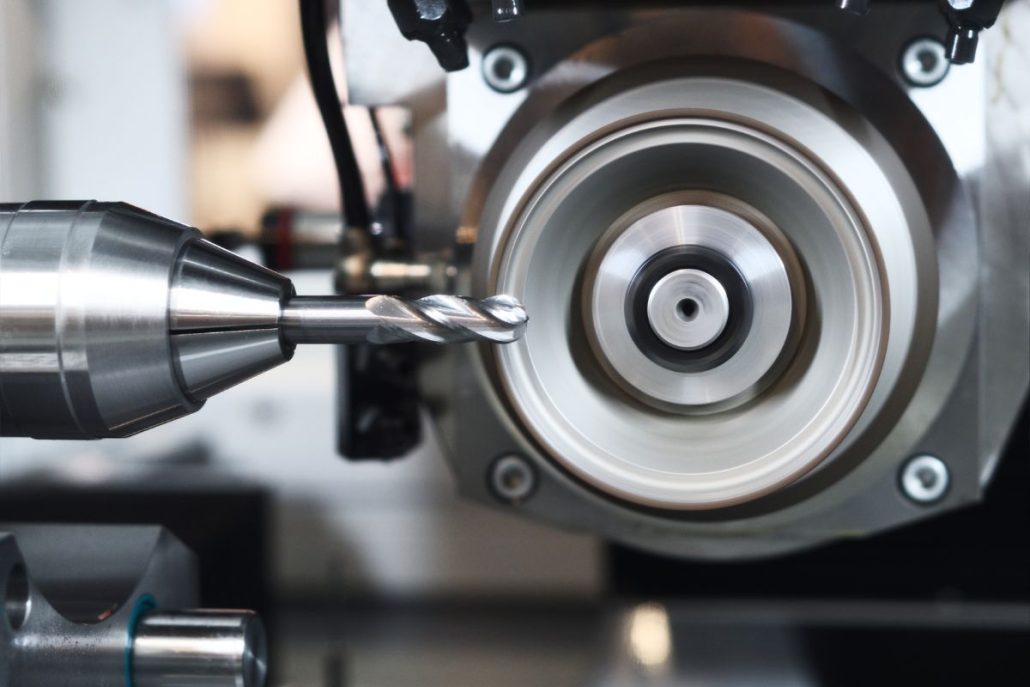
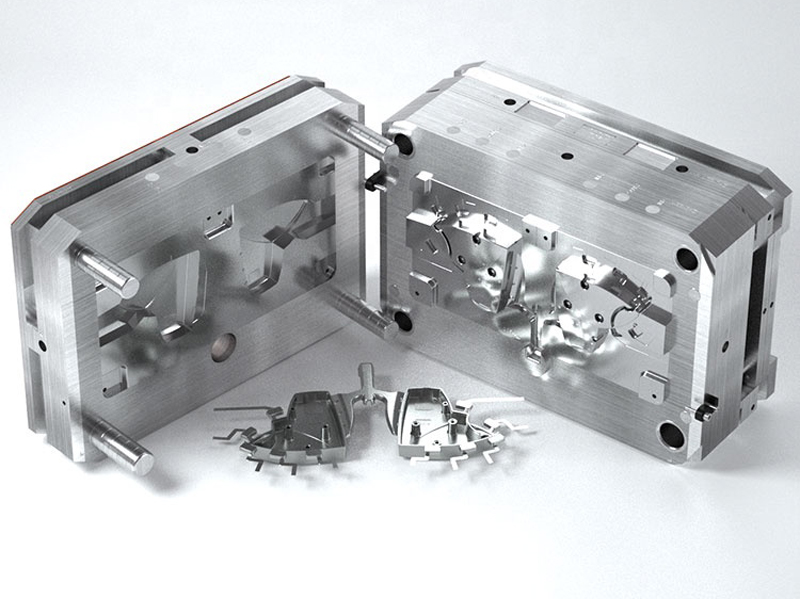
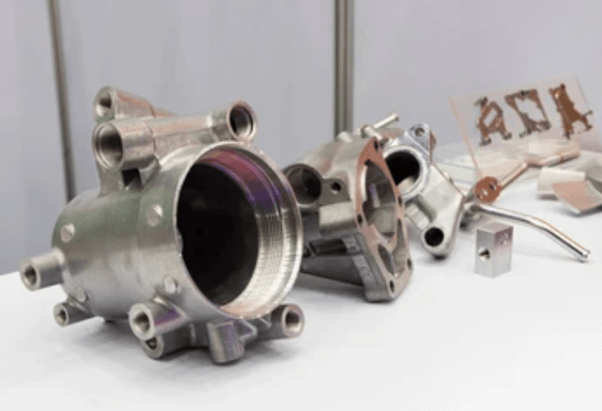
aluminiu turnatTurnarea sub presiune a zincului este un proces de fabricație care implică producerea de piese metalice complicate și puternice folosind zinc topit. Aceasta este una dintre cele mai economice și eficiente modalități de a realiza componente de înaltă calitate cu o precizie dimensională ridicată. Este un proces de injectare a zincului topit într-o matriță de oțel sub presiune ridicată pentru a crea piese care sunt puternice, ușoare și rezistente la coroziune. Caracteristicile turnării sub presiune a zincului o fac potrivită pentru utilizarea în industrii precum industria auto, electronică, aerospațială, bunuri de consum și echipamente industriale. În lumea actuală a producției, companiile de turnare sub presiune a zincului sunt esențiale, deoarece furnizează componente de înaltă calitate, proiectate cu precizie, exact ceea ce au nevoie industriile. Majoritatea acestor tipuri de companii se specializează în crearea de piese cu forme sofisticate, suprafețe fine și toleranțe strânse. Pe lângă producția de componente de înaltă performanță turnate sub presiune, majoritatea producătorilor de zinc turnat sub presiune oferă, de asemenea, servicii cu valoare adăugată, cum ar fi proiectarea, sculele, prelucrarea și finisarea pentru a satisface cerințele clienților. Piața de turnare sub presiune a zincului este larg răspândită în întreaga lume, din America de Nord până în Asia și Europa, iar companiile își pun la dispoziție expertiza, progresele tehnologice și capacitățile de producție. Companiile din aceste regiuni sunt cunoscute pentru inovație, calitate și durabilitate în procesul de producție. Folosind echipamente de ultimă generație și tehnologii avansate, acestea garantează că fiecare produs va fi la cel mai înalt standard în ceea ce privește rezistența, durabilitatea și precizia. Turnarea sub presiune a zincului este extrem de importantă deoarece este procesul central de producție a componentelor care permit funcționalitatea multor produse pe care le folosim zilnic. Companiile de turnare sub presiune a zincului sunt furnizori importanți pentru industriile care au nevoie de piese auto, cum ar fi angrenaje și componente de motor, carcase electronice și dispozitive medicale. Se preconizează că cererea de componente de înaltă calitate, cu costuri reduse, va continua să crească, iar aceste întreprinderi de turnare sub presiune a zincului vor fi liderii în materie de inovare, dezvoltare de produse și practici de durabilitate în industria turnării sub presiune. Următoarele secțiuni vor acoperi unii dintre principalii jucători din industria de turnare sub presiune a zincului, capacitățile acestora și modul în care contribuie la piața de turnare sub presiune a zincului. Ce este turnarea sub presiune a zincului? Procesul de fabricație al turnării sub presiune a zincului constă în injectarea zincului topit sau a unui aliaj de zinc sub presiune ridicată într-o matriță sau matriță de oțel prestabilită. Aceasta se solidifică rapid într-o piesă metalică detaliată și uniformă, fără prea multe prelucrări ulterioare. Procesul, care este foarte rapid, precis și capabil să producă piese metalice ușoare care sunt suficient de puternice, se numește astfel. Datorită proprietăților neobișnuite ale zincului, cum ar fi punctul său de topire scăzut și fluiditatea ridicată, cu ajutorul zincului se pot realiza modele complicate care sunt dificil de produs cu alte metale. Caracteristicile cheie ale turnării sub presiune a zincului: Deoarece este repetabil și poate produce cantități mari de piese identice cu foarte puține variații, procesul este utilizat pe scară largă în producția de masă. Istoria și evoluția turnării sub presiune a zincului Istoria turnării sub presiune a zincului datează de la începutul secolului al XIX-lea. Odată cu evoluția în timp, procesul a trecut printr-o mulțime de evoluții odată cu avansarea materialelor, a utilajelor și a tehnicilor de fabricație. Primele evoluții (secolul al XIX-lea) Primele procese de turnare sub presiune au avut loc în anii 1830 și au fost utilizate pentru a produce caractere mobile pentru prese tipografice. Deși o industrie tipografică importantă a existat încă din cele mai vechi timpuri, introducerea turnării sub presiune a schimbat substanțial industria tipografică, făcând fabricarea pieselor metalice mai rapidă și mai exactă. Creșterea în secolul XX Până la începutul anilor 1900, turnarea sub presiune s-a extins dincolo de industria tipografică, către alte industrii, cum ar fi industria auto și cea a bunurilor de consum. Produsele turnate sub presiune mai rezistente și mai versatile au fost inventate în anii 1920, când au fost inventate aliajele de zinc și aluminiu. Turnarea sub presiune a zincului a fost cu atât mai esențială în timpul celui de-al Doilea Război Mondial cu cât producătorii aveau nevoie de componente ușoare, rezistente și de înaltă precizie pentru producția militară și aeronautică. După război, tehnologiile de turnare sub presiune au crescut odată cu expansiunea creșterii industriale postbelice. Progresele moderne (secolul XXI) În prezent, inovațiile de ultimă oră, cum ar fi mașinile automate, proiectarea asistată de calculator (CAD) și imprimarea 3D pentru dezvoltarea de modele, există în utilizarea zincului turnat sub presiune. Utilizarea zincului reciclat a sporit, de asemenea, eforturile de sustenabilitate, ceea ce a făcut ca turnarea sub presiune să fie mai ecologică. Cu toate acestea, datorită Industriei 4.0, producătorii se alătură roboticii, controlului autonom al calității AI și monitorizării datelor în timp real pentru a spori eficiența producției și a reduce defectele. Aceasta este ceea ce a făcut ca turnarea zincului sub presiune să devină o parte atât de importantă a producției moderne. Importanța turnării sub presiune a zincului în producția modernă Turnarea sub presiune a zincului este o parte importantă a multor industrii, deoarece oferă producătorilor o modalitate fiabilă, eficientă și rentabilă de a produce piese proiectate cu precizie. Ca atare, ea devine din ce în ce mai importantă pe măsură ce industriile necesită componente mai ușoare, mai puternice și mai complexe pentru aplicațiile moderne. 1. Industria automobilelor În sectorul automobilelor, zincul turnat sub presiune este utilizat pe scară largă pentru producție: Durabilitatea, proprietățile ușoare și rezistența la coroziune ale zincului fac ca aceste piese să fie mai eficiente și mai durabile, ceea ce, la rândul său, face ca vehiculele să fie mai eficiente și mai durabile. 2. Electronică și telecomunicații Zincul este un material preferat pentru dispozitivele electronice datorită conductivității sale termice și electrice excelente. Următoarele utilizări ale pieselor turnate sub presiune din zinc: 3. Bunuri de consum și electrocasnice Componentele turnate sub presiune din zinc sunt utilizate în multe produse de uz casnic de zi cu zi, cum ar fi: Producătorii pot produce componente durabile și plăcute din punct de vedere estetic, cu finisaj de suprafață neted, folosind turnarea zincului sub presiune. 4. Aplicații industriale și aerospațiale Turnarea sub presiune a zincului duce, de asemenea, la producerea de piese de înaltă precizie, ușoare, care pot rezista în medii dure și la temperaturi extreme și care își găsesc utilizarea în aplicații industriale și aerospațiale. Aceste piese sunt piese critice pentru siguranță și fiabilitate în zona critică. 5. Beneficii pentru mediu și sustenabilitate Zincul este un metal complet reciclabil, astfel încât se produc mai puține deșeuri și se reduc costurile de producție și sustenabilitate. Turnarea sub presiune a zincului necesită un consum mai redus de energie decât alte metale și, prin urmare, este o opțiune ecologică pentru producția de masă. Procesul de turnare sub presiune a zincului Există mai multe etape critice în turnarea sub presiune a zincului: 1. Matrița de oțel este acoperită cu un lubrifiant pentru a facilita eliberarea pieselor turnate în timpul pregătirii matriței. 2. Zincul topit este injectat în