One of the most popular manufacturing processes for producing high-precision metal parts on a large scale is tlakové lití hliníku. It is important in contemporary industries that require high precision in dimensions, mechanical strength, light weight, and cost-effectiveness.
High-pressure steel molding of molten aluminum alloy allows manufacturers to produce complex shapes with high surface finish and reduced secondary processing. This feature makes tlakové lití hliníku one of the best options for automotive, electronics, industrial machinery, medical devices, and consumer goods.
In recent decades, tlakové lití hliníku has undergone significant advances driven by advances in alloys, tooling design and development, automation, and control systems. It is now both a mass-production technique and a highly controlled process that can accommodate close tolerances, exacting performance requirements, and international quality standards, including ISO 9001 and IATF 16949.
Obsah
PřepínáníThe Die Casting Process of Aluminum
General Rule of Die Casting of Aluminum
Aluminum die casting is a process of metal forming in which molten aluminum alloy is pressurized into a hardened steel mold, or die. The pressure is typically between hundreds and thousands of bars, and the molten metal is made to fill the smallest and most complex features of the mold. After injection, the metal cools and solidifies quickly, taking the shape of the die cavity. Once it is solid, the mold is opened and the completed casting ejected.
The use of reusable steel distinguishes die casting dies from other casting processes, such as sand casting or gravity casting. This reusability enables uniform part quality, high production efficiency, and high repeatability at large production volumes.
Processes in the Die Casting of Aluminum Production
Hliníkové tlakové lití is a very efficient manufacturing process because it produces complex, precision metal parts used in the manufacturing of automotive, electronic, and industrial equipment. It is done by pumping molten aluminum into a highly manufactured mold under high pressure, followed by finishing and quality inspection.
The summary of the process of aluminium die casting is as follows:
| Process stage | Explanation |
| Mold design | The steel dies are manufactured with cavities and vents. These dies decide the final shape and structure of the product. |
| Melting | The melting point of aluminum is around 650–700 °C. The furnace is heated to this temperature to melt aluminum. |
| Injection | The process of injecting melted aluminum is kept very precise. This means the process is done at very high pressure and speed. |
| Cooling and solidification | A dense, precise structure forms as the melted aluminum cools. |
| Vyhazování | Ejector pins push the solidified casting out of the mold. |
| Trimming and finishing | The excess of the material is removed from the structure to give it a finished look. |
Part Design Analysis
Die casting is used in aluminum casting, and the initial step is analyzing the part design. Engineers consider wall thickness, draft angles, and the location of gating and venting to identify potential obstacles and enhance manufacturability. This will address defects and casting quality.
Die or Mold Design
In the analysis, engineers design a die-casting mold with cavities, cores, slides, and parting lines. Mold design should be done properly to achieve the correct geometry, proper metal flow, and easy part ejection.
Tooling, Manufacturing, and Material Selection
Die casting molds are typically made from high-quality tool steels such as H13, DIN 1.2344, 8407, and P20, which are hard, wear-resistant, and thermally conductive. After the selection of materials, molds are produced through high-precision machining processes such as CNC milling, drilling, and EDM, and then subjected to a very stringent inspection.
Tavení a vstřikování
Melting of aluminum alloy bars occurs in a furnace at 650-700 °C. A high-speed, high-pressure plunger or hydraulic piston is then used to inject the molten aluminum into the die cavity. This high-speed injection fully covers the molds.
Cooling, Solidification, and Ejection
The die is filled with molten aluminum, which cools and solidifies after injection. The cooling rate is important to control; otherwise, too fast results in porosity, and too slow results in distortion. Channels in the die help maintain uniform temperature. When hardened, ejector pins and plates force the part out harmlessly without injuring the part or the mold.
Surface Finishing, Machining, and Trimming
Trimming is performed manually or automatically to remove excess material, including flash, runners, and burrs. Others are then CNC-machined to achieve very fine tolerances or to add ornamentation, such as threaded holes. Surface finishing can enhance durability and appearance through anodizing, powder coating, painting, electroplating, or electrophoresis.
Final Assembly and Quality Inspection
As a pre-delivery step, each aluminum casting die part undergoes thorough quality inspection to meet the customer’s specifications. It can also be assembled upon completion of the product, as needed, thereby delivering high-quality products that meet global standards.

Types of Aluminum Die Casting Processes
Vysokotlaké tlakové lití
The most widely used aluminum die-casting process is high-pressure die casting. It employs cold-chamber horizontal machines, in which molten aluminum is injected into the die at extremely high pressure and speed.
This is the best process for making fine-walled, complex objects with high surface quality and close tolerances. Die casting is commonly applied at high pressure in the automobile, electronics, and industrial sectors.
Nízkotlaké tlakové lití
Low-pressure die casting is a process that injects molten aluminum into the mold at low pressure, compared to high-speed injection. In this process, greater control over metal movement and reduced turbulence result in higher internal quality and lower porosity.
Die-cast aluminum is often done at low pressure to create structural parts and wheels whose mechanical integrity is of high importance.
Vakuové tlakové lití
It is a high-pressure die casting, but in a sophisticated form in which air is removed from the mold cavity before and during injection: vacuum die casting.
This process can greatly reduce porosity and enhance mechanical properties by minimizing trapped gases, making the castings suitable for heat treatment and welding.
Technical Considerations for Aluminum Die Casting
| Parameters | Typical range |
| Injecting pressure | 1000-30,000 Psi |
| Tloušťka stěny | 1.5–5.0 mm |
| Dimensional tolerance | ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm |
| Životnost nástroje | 100,000 – 1,000,000+ shots |
| Part Weight Range | A few grams up to 30 kg |
| Surface Roughness | Ra 1.6–3.2 μm |
Die Casting Alloys of Aluminum
Significance of Alloy Selection
Due to the high performance of an aluminum die-casting component, the alloy is a major determinant of its performance. Several die-cast slitiny hliníku differ in strength, ductility, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and machinability. The choice of alloy is vital for ensuring functional requirements are met while minimizing cost and improving manufacturability.
| Types of Aluminum alloy | Vlastnosti | Aplikace |
| A380 | Excellent fluidity, good strength | Automotive housings, electronics |
| A383 | High strength and hard | Electrical enclosures, consumer products |
| A360 | High ductility, pressure tightness | Automotive components |
| ADC12 | Excellent castability and fluidity | Engine brackets, machinery parts |
| A413 | Excellent corrosion resistance | Aerospace and structural components |
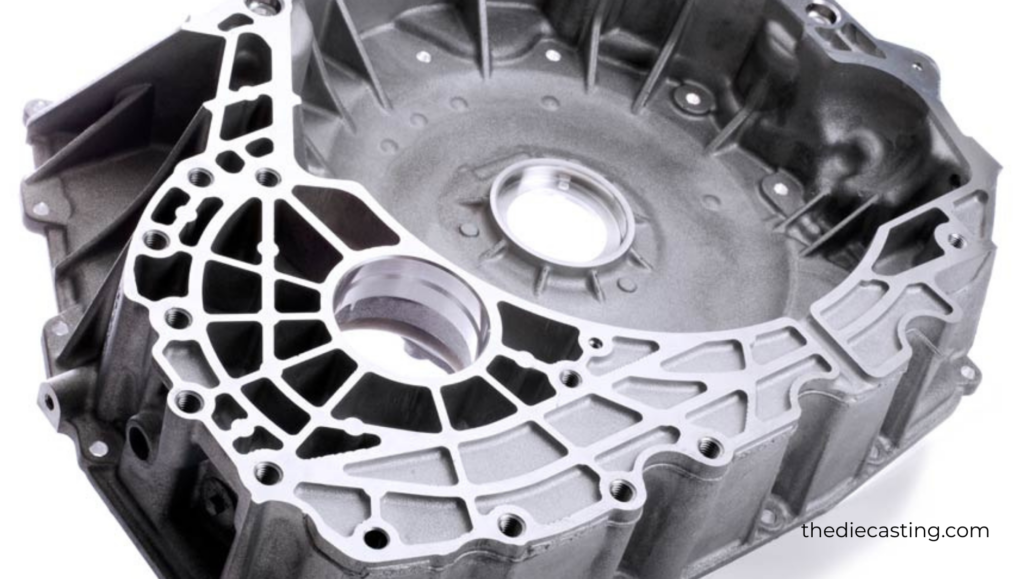

Design Considerations for Aluminum Die Casting
Design for Manufacturability
The first step to successful aluminum die casting is a well-designed part. The engineers should pay attention to the behavior of metal flow, cooling, and ejection. Wall thickness should be uniform to achieve uniform cooling and minimize the likelihood of porosity, shrinkage, and distortion.
Easy connections between the thick and thin parts enhance casting integrity and dimensional accuracy. Vertical surfaces are provided with draft angles that facilitate easy ejection from the die.
The parts can be deposited in the mold, causing surface damage or tool wear when there is inadequate draft. Instead of sharp corners, fillets and radii are used, which minimize stress concentration and enhance the flow of metal during injection.
Tolerance and Surface Finish Expectations
Aluminum die casting offers high dimensional accuracy compared to many other casting processes. Common tolerances range from -0.05mm to -0.2mm, depending on the part’s size and geometry.
Surface finishes are smooth and even, often eliminating the need for extensive machining or polishing. Nevertheless, threaded holes, sealing surfaces, or bearing seats may still be critical features and may require CNC machining.
Control in Aluminium Die Casting
Process Control Techniques
The manufacturer must ensure consistent quality in tlakové lití hliníkuand maintain tight process control at all stages of production. Melt temperature, injection rate, pressure, cooling rate, and die temperature are constantly checked and adjusted.
Plants well equipped with technology feature real-time monitoring systems and automated controls to minimize variation. The inspection methods are visual inspection, dimensional inspection using a coordinate measuring machine, X-ray inspection to detect internal porosity, hardness testing, and chemical composition testing.
These precautions are taken to ensure that all batches of castings comply with the customer’s and industry’s specifications and requirements.
Certifications and Standards in the industry
Manufacturers of quality-based aluminum die-casting have also been certified under the internationally recognized quality management systems. All three certifications (IATF 16949, ISO 14001, and ISO 9001) demonstrate the company’s commitment to quality, environmental management, and continuous improvement, which automotive and industrial customers highly value.
Final Finishing of Surfaces and Operations
Machining and Trimming
Casting requires removing solid waste, e.g., runners, gates, and flash. Pruning can either be done manually or through automated trim presses.
When higher tolerance or more specialized functions are required, CNC machining is employed. The machining centres nowadays are highly accurate, dependable, and highly repeatable across high-volume production.
Surface Treatment Options
Die-cast aluminum may also receive various surface finishes to enhance looks, corrosion resistance, and functionality. The common ones are electroplating, electrophoresis, anodizing, powder coating, and painting. The intended use, aesthetics, and affordability determine the finish type.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Aluminum Die Castings
Die Casting of Aluminum: Benefits
The ideal process is aluminum die casting, as it offers light weight and mechanical strength, making it suitable for cases that require weight reduction. The process offers efficiency in production and stability, as well as the ability to produce complicated geometries at reduced waste.
Other aspects that make aluminum attractive as a sustainable manufacturing material include its inherent corrosion resistance and recyclability.
Cons and Concerns
Aluminum die casting is limited, though it has advantages. Initial tooling can be costly and less cost-effective when production volume is very low.
It is also usually limited to some classes of aluminum alloys, and the inability to control the process can lead to defects, such as porosity or size variation. These issues have been addressed through good design, engineering, and high-quality systems.
Aluminum Die Casting: Industrial Applications
Automobile and Transportation
The automotive industry is one of the largest users of aluminum die casting. Part of which can be used to exploit aluminum’s strength-to-weight ratio to enhance fuel economy and reduce emissions are engine blocks, transmission housings, brackets, and structural parts.
Electronics and Electrical Equipment
The thermal and electrical conductivity of aluminum is exceptional, which is why electronic housings, heat sinks, and enclosures are often cast in it. These properties prioritize effective heat dissipation and electromagnetic shielding.
Machinery, Consumer Products and Industry
Industrial equipment, power tools, lighting, and household appliances are cast in aluminum die casting because it produces components that are strong, accurate, and visually appealing. Process facilitates performance (functional) and current product design.
Závěr
Hliníkové tlakové lití is one of the most promising and reliable methods for producing high-quality, lightweight, durable metal components at large-scale production. High pressure to force a reusable steel die into molten aluminum alloys enables manufacturers to produce complex geometries, tight dimensional tolerances, and premium surface finishes with minimal secondary operations.
All this underscores the need for aluminum die casting across many sectors, including cars, electronics, industrial equipment, medical equipment, consumer goods, and others. Advances in alloy development, die design, automation, and process control have also helped improve the uniformity, quality, and performance of die-cast aluminum components.
Producers can select the process that meets their structural, mechanical, and aesthetic requirements, with options including high, low, and vacuum aluminum die casting. Adequate attention to part design, alloy selection, tool quality, and inspection will help eliminate typical challenges, such as porosity or high tooling costs.
In general, the combination of strength, weight reduction, cost efficiency, and sustainability is an ideal solution for aluminum die casting. It can be easily recycled, is corrosion-resistant, and meets current quality requirements, making it one of the significant technologies for meeting the demands of high-performance, high-volume production environments in the modern world.










