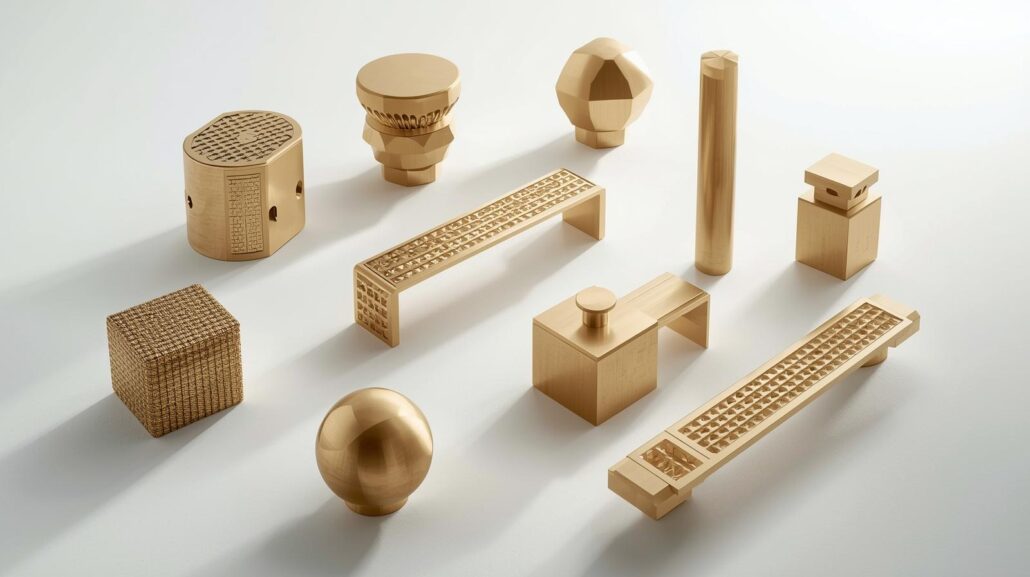
Cabinet hardware can be viewed as minor detail, yet it can change the appearance and functionality of a room. Of the numerous finishes that can be used, the brass cabinet hardware is a test of time in terms of beauty, strength, and versatility. Considering remodeling the kitchen, upgrading the bathroom vanity, or even refreshing the storage furniture, the brass finish is the one that will be durable and, at the same time, very stylish. Both designers and homeowners still prefer the useof brass hardware as it has added significance to modern and traditional interiors. Its warm tones, which are of gold, also match well with wood, stone, or painted cabinets, making it one of the most adaptive finishes. As simple, modern pulls as fancy, vintage knobs, brass cabinet hardware is a feature that gives the whole design of a space an upscale look. Brass, unlike other metals, is a good-looking item, but it provides long-lasting value. The quality of brass kitchen hardware and brushed brass hardware resists corrosion, can be used in everyday life, and acquiress the status of timeless. Such a blend of style and performance makes brass an investment that enhances the appearance and functionality of the cabinets so that they are refined over the years to come. History and popularity of Brass in Design Brass is a copper-zinc alloy and has been applied in various structures, furniture, and ornaments forcenturies. Brass used to be a common decorative fitting and fixtureas it was deemed highly beautiful and elegant once. The brass hardware is also still used in the present daydue to its appearance and its durability and strength, and it is also used in the current-day interiors due to the practicality in its usage and its appearance,, which is more than impressive. The timeless quality of the brass cabinet hardware is its flexibility. It may be shined brightly and reflective like a mirror, or it may have a more subdued look and be finished in muted colors. Since the shift of interior decor towards warmer metallics, brass remains one of the finishes that can be mixed with light and dark cabinets. What does Brass Cabinet Hardware mean? Brass cabinet hardware is knobs, pulls, hinges, handles, and other fittings manufactured out of the alloy of copper and zinc, known as brass. Such hardware is very common in the kitchen, bathroom, and furniture since it is strong, durable, and not out of fashion. Compared to cheaper metals, brass does not corrode and will naturally age with a patina, and it can be polished, left in a satin finish, or antique, or left in the so-called brushed brass hardware. The designers and owners of homes prefer the use of brass hardware due to its diversity. Specifically, brass kitchen hardware is functional and stylish, and it has become one of the most popular options to upgrade the cabinets. Types of Brass Hardware Cabinet accessories come in an array of different forms made out of brass, with each being used in a different way. The most popular ones are: In any design project, brass cabinet hardware, regardless of its type, is a useful addition in terms of decorative and functional purposes. The manufacturing of Brass Cabinet Hardware The production of so-called brass cabinet hardware is a long-stage product manufacturing process based on the requirements of durability, usefulness, and beauty. It is a process that uses a mixture of both traditional and modern metal finishing techniques. Alloy Preparation It starts with the melting of a mixture of copper and zinc to form brass. Additional elements can be added depending on what finish is desired. This makes the brass hardware with the correct strength, machinability, and color. Casting or Forging After preparation of the brass alloy, it is then cast (molten brass poured into castings) or forged (pressed and heated brass compressed into castings). Copies of brass kitchen hardware are more powerful and sturdier. Machining and Shaping These are then turned into accurate shapes, knobs, pulls, handles, or hinges. CNC machines and old-fashioned lathes tend to build uniformity in the so-called brass cabinet hardware. Surface Finishing When the pieces have been shaped, they are automatically ground and polished to a smooth finish. Finishes applied at this stage include polished, antique, satin, or brushed brass hardware to give it the desired appearance. Plating or Coating (Optional) In other instances, a protective coating of lacquer or further plating is made to increase resistance to corrosion. It is common to leave solid brass unlacquered in the natural patina style. Mechanical Assembly and Quality Control Lastly, the quality, fit, and finish of every item of the brass cabinet hardware are checked. Assembling screws and fittings and packaging them are done before distributing. Advantages of Brass Cabinet Hardware Durability Brass is a material that has been known to have strength and endurance. Solid brass, unlike cheaper alloys does not bend, bend, and break, meaning your cabinets will be useful over time. It is particularly significant that brass kitchen hardware has to stand up to daily wear. Timeless Aesthetics Interiors are made warm and rich with the golden hues of brass. It has smooth finishes and polishing that is elegant, and the hardware is brushed brass, giving it a modern, subtle look. Corrosion Resistance The inherent nature of brass is such that it is resistant to tarnish and corrosion and should therefore be used in the kitchen and bathroom where moisture is abundant. Versatility Ranging from coarse farmhouse kitchens to polished modern bathrooms, brass cabinet hardware goes well with all kinds of styles. It has been flexible, which is why it is still used in various projects of brass hardware by designers. Usage in Bathrooms and in Kitchens One of the most noticeable details in the kitchens and bathrooms is cabinet hardware, where functionality and design should be in harmony. Brass cabinet hardware offers the strength needed in busy areas, as well as serving as a decorative center stage. Kitchens The contemporary kitchen styles are more than pleased with the