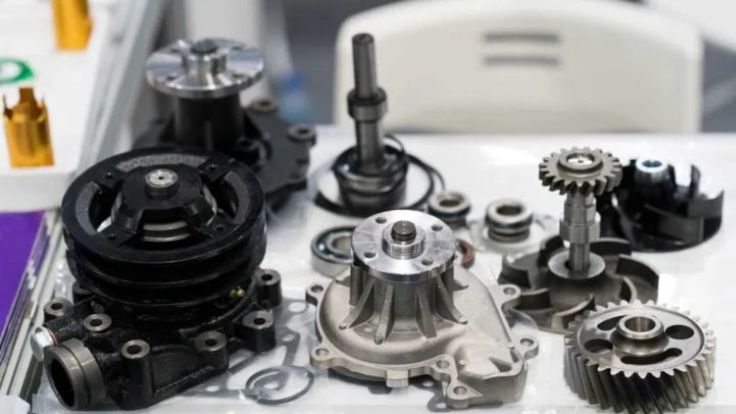
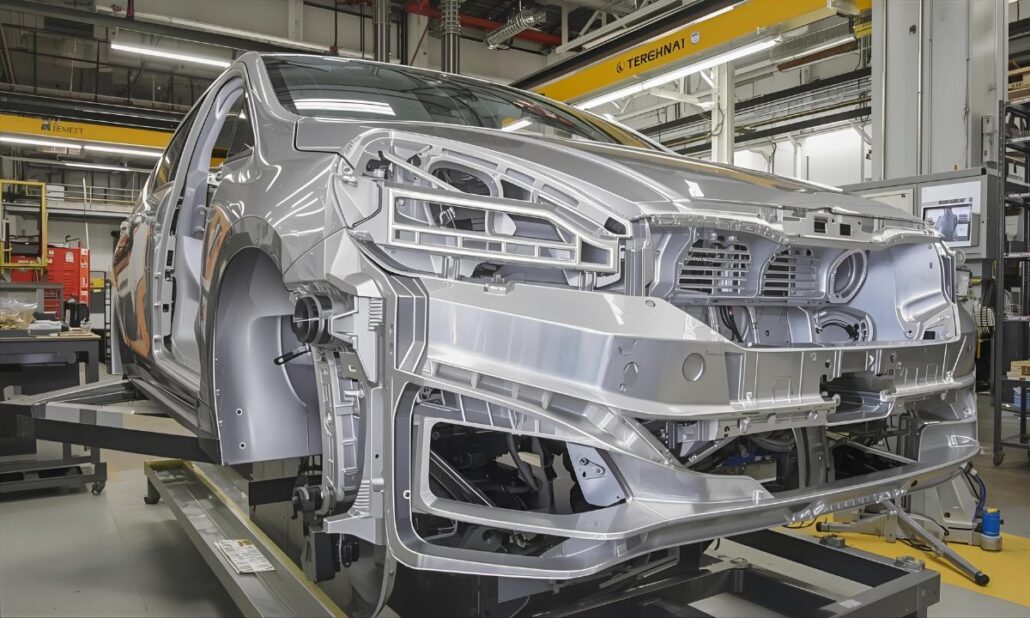
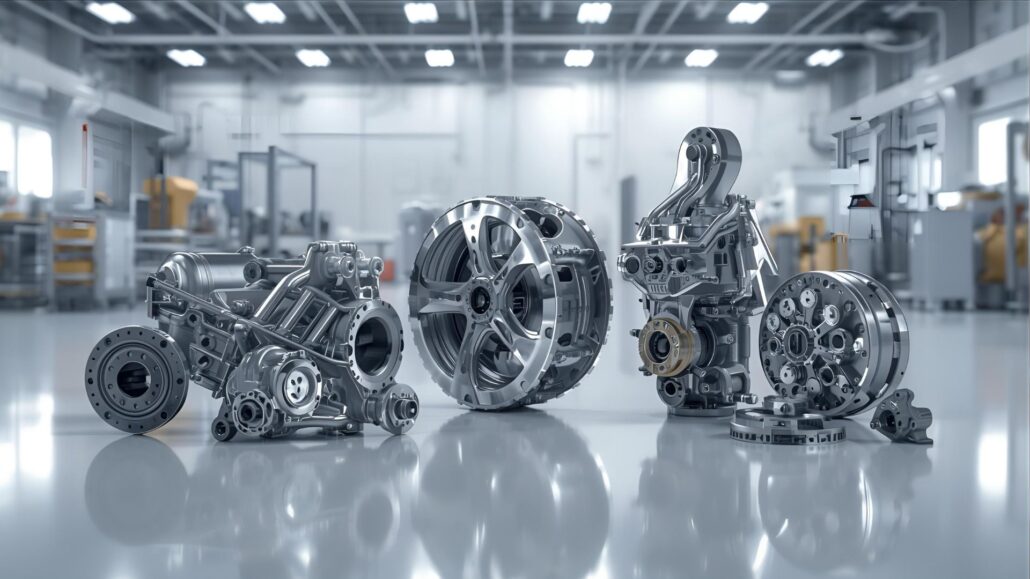
The modern automobile is a sophisticated machine that consists of thousands of separate parts with their own purpose to provide safety, performance, and reliability. Casting is one of the various manufacturing processes that are employed in the automotive industry. Casting is now an irreversible procedure where major parts of a vehicle are formed by shaping molten metal into extremely detailed and strong parts. The engines, transmissions, and braking systems of most vehicles are among the most significant systems that require parts made by casting. Indeed, when designers and builders discuss efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness in the production, casting of automobile parts are often at the centre stage of the debate. The art of casting is not new; it was invented thousands of years ago. However, its application in the motor industry has undergone a revolutionary shift to harness hi-tech technologies and the most recent alloys that can fit the high demands of the modern car. Casting has been instrumental in enabling cars to maintain high-performance standards at a relatively low cost through lightweight aluminum engine blocks that are tough and, resilient cast-iron brake components. The article will review the history of the automobile casting parts, processes, advantages, and future trends of automobile casting parts and reveal the reasons why the automobile casting parts continue to be a pillar in the automotive manufacturing industry. History of Casting It was actually the aluminum casting process that penetrated the sphere in the middle of the 20th century. Casting has been in use in vehicles since the late 19th and early 20th centuries, when the automobile was first developed to replace the horse-drawn carriage. Early engines demanded powerful but inexpensive parts, and casting was the right way to go. One of the first methods to make engine blocks, crankshafts, and housings was iron casting. With the increase in the automobile industry, casting techniques increased and became advanced. The automobile manufacturers learned that they could increase fuel efficiency without reducing the lifetime of the vehicles due to lighter engines and structural parts. Casting is applied to different systems of vehicles in accordance with their application and importance. Finally, the automobile casting parts have the important role of giving strength, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness to reduce the cost, which is why automobile parts are the giants of the automotive industry. What are Automobile Casting Parts? Automobile Casting Parts can be defined as parts of a vehicle that are produced through pouring molten metal into a mold, and the resulting molten metal hardens into a desired shape. This has enabled the manufacture of robust, sturdy, and intricate components that are utilized in automobiles, including engine blocks, cylinder heads, transmission housings, brake drums, and wheels. They are very popular since casting offers: Taking the case of an engine block, the block has various chambers and coolant passages with threaded openings that can be cast correctly. What is Casting? The process of casting is a type of manufacturing where molten metal is poured into a mold and allowed to cool in the shape of the mold. After cooling, the casting is removed, machined (where needed),, and fitted into the finished product. It is an operation in which it is possible to produce both strong and geometrically complex parts. The reason why automobile manufacturers like to use casting is that they can produce large quantities of complicated parts of uniform quality. The proper melting temperature should also be maintained to remove defects such as porosity or underfill We are discussing not only structurally significant parts of automobiles, but also those that must be precise and durable under severe conditions of high temperatures, pressures, and constant wear. Process of Casting in Automobile Parts High-volume production also automates machines or high-pressure systems to ensure a high level of accuracy and consistency. 1. Pattern Making It starts with the production of a pattern, an imitation of the finished part. Patterns tend to be made of wood, metal, or plastic. They also determine the accurate shape and size of the mold cavity into which the molten metal will be poured. 2. Mold Preparation Sand, metal, or ceramic materials are used to form a mold. The two halves of the mold make the cavity to shape the part. Hollows can also be introduced within the mold,, such as internal passages within an engine block. 3. Melting the Metal In a furnace, a controlled temperature is used to melt the selected metal or alloy (cast iron, aluminum, or magnesium). This is to bring mechanical properties to high-performance applications such as engines or gearboxes. 4. Pouring When the metal is melted, it is filled into the mold. The proper sizes and finishes are ensured during drilling, milling, and turning. 5. Solidification and Cooling The heated material is left to cool and harden within the mold, assuming the shape of the mold. The part should avoid a shrinkage defect or crack due to uncontrolled cooling rates. 6. Mold Removal When solidifying, the mold is broken (in sand casting) or the mold is opened (in permanent and die casting). A raw casting is then removed and processed further as a casting blank. 7. Fettling and Cleaning Unneeded material, including sprues, risers, or flash, is eliminated. The casting could be shot blasted or ground to clean up the surface to make it easy to machine. 8. Heat Treatment (if required) Cast parts can be heat-treated to enhance their strength, hardness, or toughness. Sand Casting – Sand casting is one of the oldest and most common ways in which a mold of sand is molded into a more complicated shape. 9. Machining and Finishing Despite the fact that casting generates near-net shapes, a lot of automobile parts have to be machined to be precise. It is used with the engine block, cylinder head, and manifold. 10. Inspection and Testing Lastly, quality checks are done on the cast part. Non-destructive testing (NDT), dimensional testing, and material inspection are conducted to ensure that the part is up to industry standards before assembly into