Difference Between Hot Chamber Die Casting and Cold Chamber Die Casting
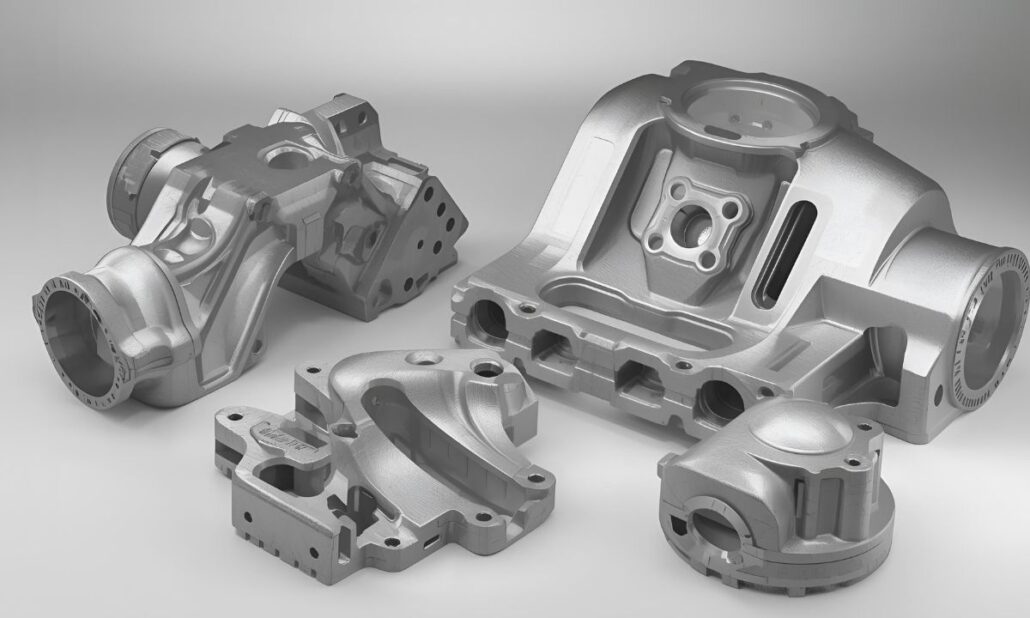
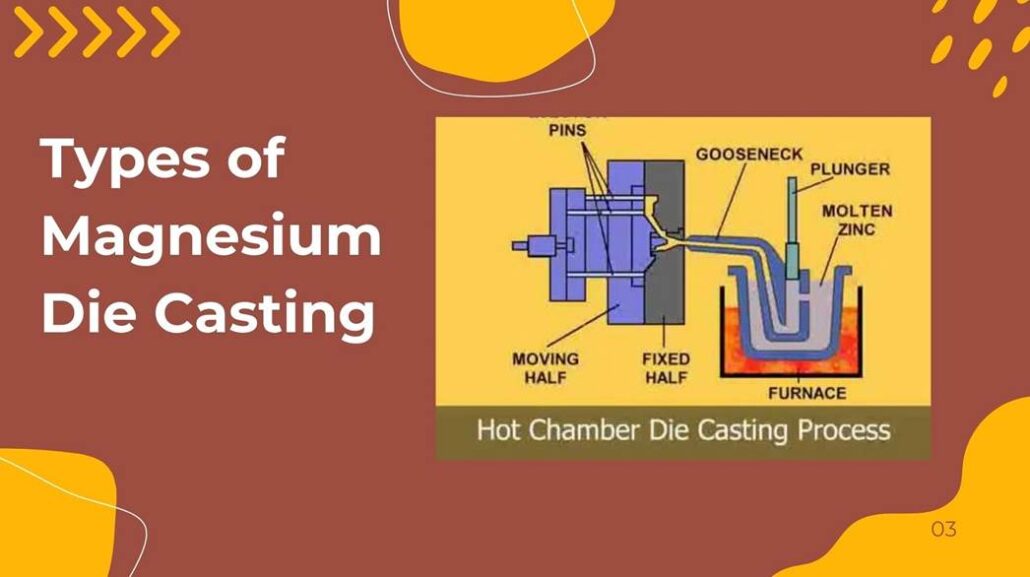
colata di alluminioDie casting is a metal casting process that uses high pressure to produce complex, high-volume, precise metal components with superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy. This is achieved by high-speed, high-pressure injection of molten metal into a hardened steel mold, known as a die. After the metal solidifies, the die is opened, and the completed component is ejected, trimmed, or lightly secondary processed. Due to its speed, reproducibility, and ability to produce thin-walled, detailed casts, die casting is widely used across the automotive, electronics, aerospace, appliance, and consumer products sectors. High-pressure die casting processes fall into two major types: hot-chamber and cold-chamber die casting. Although both processes use pressure to force molten metal into a die, the ways the metal is melted, manipulated, and injected differ markedly. The differences influence the type of metals used, cycle time, production cost, tooling life, and part size. Hot-chamber die casting integrates the melting furnace with the casting machine, enabling faster processing and improved suitability for low-melting-point alloys. In cold-chamber die casting, however, a separate furnace is used, and molten metal is poured into the machine each time. This arrangement is preferable when the alloy has a higher melting point, e.g., aluminum and copper. Knowledge of the differences between these two processes helps Die Castings China select the most effective, cost-effective, and technically viable method for the company’s application. Hot Chamber Die Casting: Process and Technical Knowledge Hot-chamber die casting is a high-pressure metal casting process primarily used for low-melting-point alloys. It has extensive applications in the automotive hardware, electronics, telecommunications, and consumer goods industries, as well as in sectors that require high production speeds, tight dimensional tolerances, and good surface finish. The key feature of this process is that the melting furnace is integrated into the casting machine. In this type of design, the molten metal is kept in a continuously ready-to-inject state, reducing handling time and resulting in production that is much more efficient than in other casting methods. Summary of the Process Process Explanation Melting Metal is maintained in a furnace inbuilt as molten at about 400 -450 °C in the case of zinc alloys and 600 °C in the case of some magnesium alloys. Filling the Gooseneck In this setup, a hydraulic plunger is used to withdraw until molten metal fills the gooseneck chamber. Injection The plunger moves forward and injects metal into the die cavity at rates up to 3060 m/s. Solidification The metal’s cooling and solidification take 2-10 seconds, depending on the part’s thickness. Ejection This is where the die opens, and the casting is removed by die ejection pins. Repeat The total cycle time is 3 to 15 seconds, enabling high production volumes. The Process of the Hot Chamber Die Casting In hot-chamber die casting, the molten metal is retained in an in-built furnace mounted on the machine. The molten metal submerges a component called a gooseneck. When the plunger is retracted, an intake port supplies molten metal to the injection chamber. The plunger is then hydraulically actuated, driving the metal through the gooseneck and into the die cavity at high velocity. The injection rates may reach 30-60 meters per second, filling the cavity before the metal solidifies. After being cast, the molten metal is pressurized and cooled. Solidification typically takes 2-10 seconds, depending on wall thickness and alloy. With the part already solid, the die is opened, and the ejector pins force the casting out. The machine thereafter shuts and initiates the subsequent cycle. Technical Parameters and the Operating Conditions The process is carried out within well-controlled temperature and high-pressure ranges to ensure tooling quality and safety. Zinc alloys can be cast at temperatures between 400 and 450 °C. In contrast, magnesium alloys can be cast at temperatures closer to 600 °C. The injection pressure is typically 7-35 MPa (approximately 1,000-5,000 psi). The die temperature is maintained between 150 and 250 °C to ensure consistent metal flow and controlled cooling. Due to the wide range of machine sizes, the clamping force typically ranges from 20 to 500 tons. Shot weights are usually less than 1 kilogram, but machines can handle up to 5 kilograms. This is one of the fastest metal-forming methods, with production rates often reaching 300-700 parts per hour due to its high cycle rate. Applicable Material Limits and Alloys Hot-chamber die casting applies only to alloys that do not attack iron at high temperatures. The most common are zinc alloys, including Zamak 3 and Zamak 5, which have melting points near 385 °C. It is also commonly used with magnesium alloys such as AZ91D, which melts at about 595 °C. It is also possible to process lead-tin alloys, but their industrial applications are more limited. This process cannot be applied to aluminum, which has a melting point of approximately 660 degrees Celsius, which can destroy the submerged injection elements. Performance Benefits and Practices Limitations Parameter Typical Range Metal Temperature 400–450°C (Zinc), up to 600°C (Magnesium) Injection Pressure 7–35 MPa (1,000–5,000 psi) Cycle Time 3–15 seconds Machine Tonnage 20–500 tons Production Rate 300–700 parts/hour Die Temperature 150–250°C Typical Part Weight 0.02–5 kg Cold Chamber Die Casting: Process and Technical Observations Cold-chamber die casting is a high-pressure metal casting process suitable for alloys with medium- to high-melting points. It is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and electronics that require strong, lightweight components with precise dimensions. This process uses a separate furnace to melt the metal, rather than a hot-chamber die casting. Each shot is moved into the casting machine with the molten metal, making the system suitable for materials that would harm a permanently submerged injection process. This geometric distinction characterizes the operating mode, production speed, and material range of the cold-chamber process. Process Overview During cold-chamber die casting, the metal is melted in an external furnace at the appropriate alloy-specific temperature. The melting temperature of aluminum alloys is generally in the range of 660- 700 °C, and copper-based alloys might be melted at temperatures exceeding 1,000 °C. After melting,