Panoramica dell'industria delle aziende di pressofusione di zinco
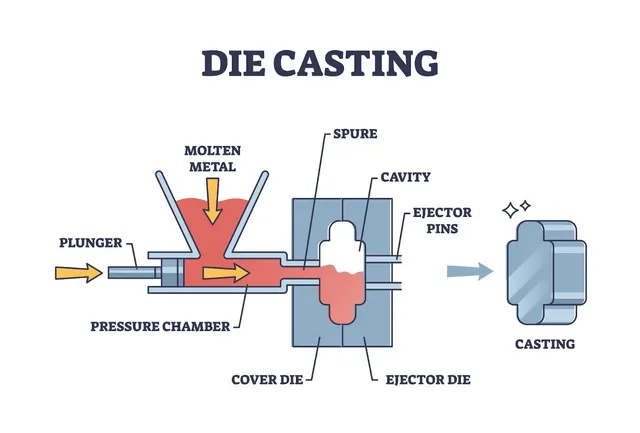
colata di alluminioZinc die casting is a manufacturing process that involves the production of intricate and strong metal parts using molten zinc. This is one of the most economical and efficient ways of making high-quality components with high dimensional accuracy. It is a process of injecting molten zinc into a steel mold under high pressure to create parts that are strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant. The characteristics of zinc die casting make it suitable for use in industries like automotive, electronics, aerospace, consumer goods and industrial equipment. In today’s manufacturing world, zinc die casting companies are critical because they provide high-quality precision-engineered components specifically what industries need. The majority of these kinds of companies specialize in creating parts with sophisticated shapes, fine surfaces, and tight tolerances. Besides producing high-performance die-cast components, most zinc die casting manufacturers also provide value-added services like designing, tooling, machining and finishing to satisfy customer’s requirements. The zinc die-casting market is spread wide across the globe, from North America to Asia and Europe, and companies are bringing their expertise, technological advancements and manufacturing capabilities to the table. The companies in these regions are known for their innovation, quality and sustainability in the manufacturing process. Using state-of-the-art equipment and advanced technologies they guarantee that each product will be of the highest standard in terms of strength, durability and precision. Zinc die casting is of utmost importance as it is the central process of producing components that enable the functionality of many products we use daily. Zinc die casting companies are important suppliers for industries that need automotive parts such as gears and engine components, electronic housings and medical devices. The demand for high-quality, low-cost components is expected to continue to rise and these zinc die casting companies are expected to be the leaders in innovation, product development and sustainability practices of the die-casting industry. The following sections will cover some of the major players in the zinc die-casting industry, their capabilities and how they contribute to the zinc die-casting market. What is Zinc Die Casting? The manufacturing process of zinc die casting is to inject molten zinc or a zinc alloy under high pressure into pre pre-designed steel mold or die. It quickly solidifies into a metal part that is detailed and uniform without much post-processing. The process, which is very fast, precise, and able to produce lightweight metal parts that are strong enough, is called this. Because of zinc’s unusual properties, such as its low melting point and high fluidity, intricate designs that are difficult to produce with other metals can be made using zinc. Zinc Die Casting Key Characteristics: Because it is repeatable and can produce large amounts of identical parts with very little variation, the process is widely used in mass production. The History and Evolution of Zinc Die Casting The history of zinc die casting goes back to the early 19th century. With the evolution over time, the process has gone through a lot of evolution with the move of the advancement in the materials, machinery and the manufacturing techniques. Early Developments (19th Century) The first die-casting processes occurred in the 1830s and were used to make movable type for printing presses. Although an important printing industry has existed since ancient times, the introduction of die casting substantially changed the printing industry by making the manufacture of metal parts more rapid and more exact. Growth in the 20th Century By the early 1900s, die casting had grown beyond printing to other industries such as automotive and consumer goods. Stronger, more versatile die-cast products were invented in the 1920s when zinc and aluminium alloys were invented. Zinc die casting was all the more essential in World War II since manufacturers required lightweight, tough and high-precision components for military and aircraft production. After the war, the technologies of die casting grew with the expansion of post-war industrial growth. Modern Advancements (21st Century) Today, cutting-edge innovations like automated machines, computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D printing for mod development exist in the use of zinc die casting. The use of recycled zinc has also increased sustainability efforts, which has made die-casting more environmentally friendly. However, due to Industry 4.0, manufacturers are joining robotics, AI autonomous quality control and real-time data monitoring to boost the efficiency of production and decrease defects. This is what has made zinc die casting such an important part of modern manufacturing. Importance of Zinc Die Casting in Modern Manufacturing Zinc die casting is an important part of many industries as it offers manufacturers a dependable, efficient and cost-effective way of producing precision-engineered parts. As such, it becomes increasingly important as industries require lighter, stronger and more complex components for modern applications. 1. Automotive Industry In the automotive sector, zinc die casting is widely used to manufacture: Zinc’s durability, lightweight properties and corrosion resistance make these parts more efficient and more durable, which in turn makes vehicles more efficient and more durable. 2. Electronics and Telecommunications Zinc is a preferred material for electronic devices due to its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. The following uses zinc die-cast parts: 3. Consumer Goods and Home Appliances Zinc die-cast components are used in many everyday household products such as: Manufacturers can produce durable and aesthetically pleasing components having smooth surface finish using zinc die casting. 4. Industrial and Aerospace Applications Zinc die casting also leads to the production of high precision, lightweight parts that can withstand harsh environments and extreme temperatures and find its use in industrial and aerospace applications. These parts are critical parts for safety and reliability in the critical area. 5. Environmental and Sustainability Benefits Zinc is a fully recyclable metal, so there is less waste produced and reduced manufacturing and sustainability costs. Zinc die casting requires lower energy consumption than other metals and is therefore an eco-friendly option for mass production. The Zinc Die Casting Process There are several critical steps in zinc die casting: 1. The steel mold is coated with a lubricant to ease the release of cast parts during mold preparation. 2. Molten zinc is injected into the