Hidegkamrás öntés: öntvények: Teljes útmutató
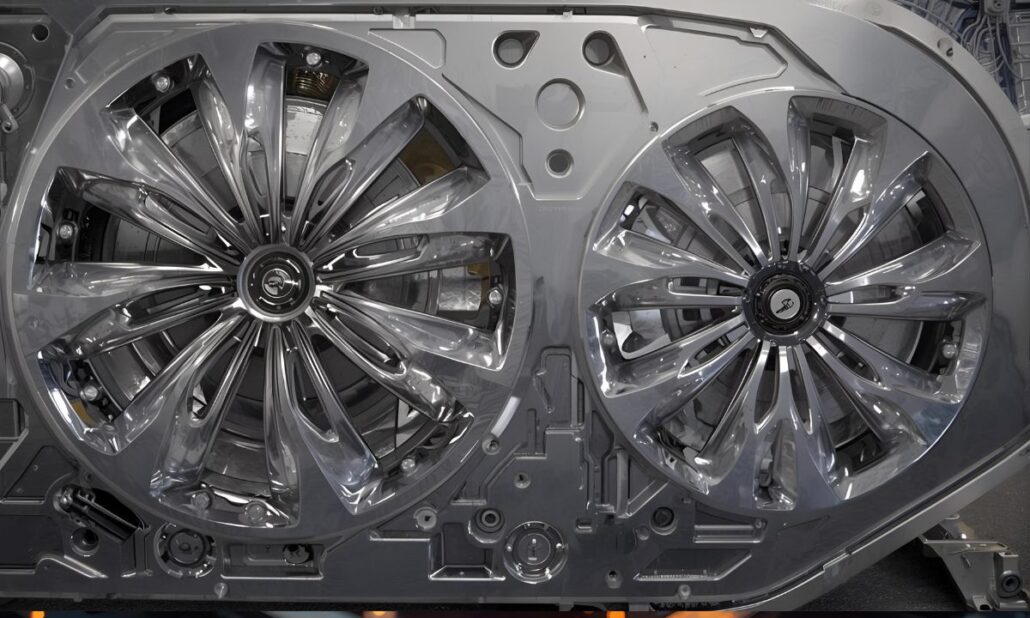
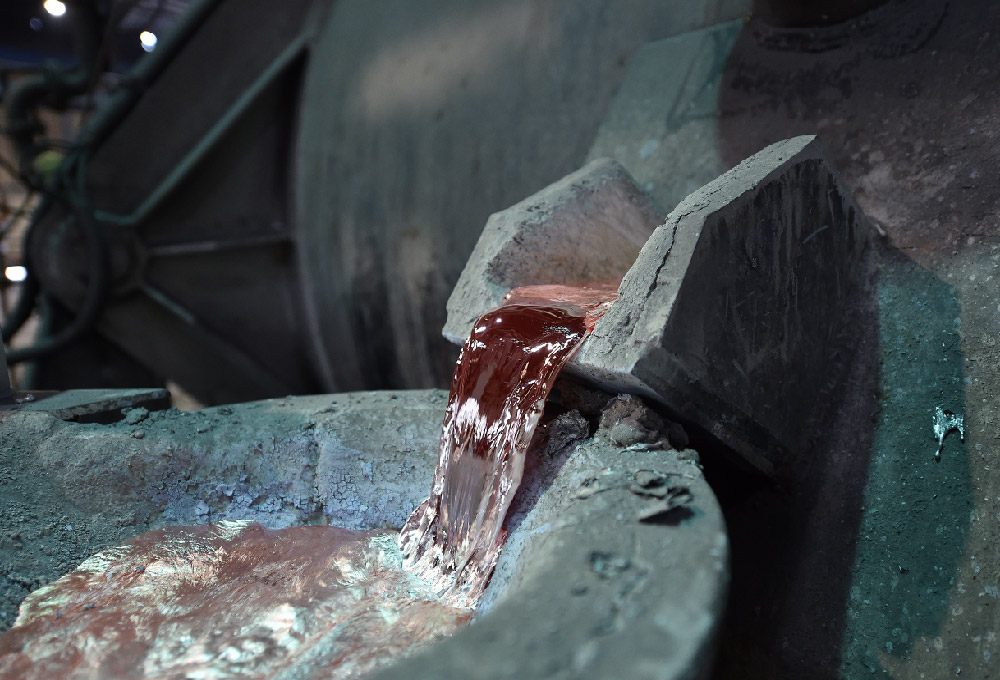
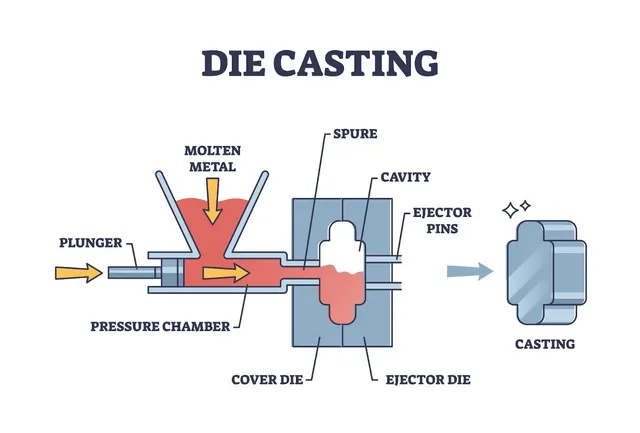
öntvényöntés, Die Casting gyártó, öntvény alkatrészekThe cold chamber die casting process is initiated by first ladling molten metal into a separate injection chamber and then forcing it out into a steel mould. This process deals with high melting alloys such as aluminium, copper and magnesium. It is a tight-tolerance, high-pressure production process found in the automotive, electronics, and industrial parts production. What is cold chamber die casting is and when to use it? Cold chamber die casting is a high-pressure moulding of metals, which would ruin or corrode a hot-chamber system. Practically, the operators melt the metal in a different furnace. Then they pour the molten metal into an unheated shot sleeve. The metal is forced into the closed mould by a hydraulic plunger with extreme pressure. The section hardens very rapidly, and the die is opened to spurt out the casting. This can be used when the alloy is of high melting temperature or where the alloy would corrode injection components, such as aluminium and copper alloys. The process sacrifices speed of the cycle for the scale and flexibility of the alloy. Cold Chamber Die Casting Process Step-by-Step Cold chamber die casting is one of the most reliable techniques for making high-quality metal parts. Every process must be monitored in terms of temperature, pressure and time. Minor variations can impact the surface finish, strength and dimensional accuracy of the end product. Melting the Metal It starts by melting the metal in a separate furnace. Mostly used are aluminium, magnesium and copper alloys. In the case of aluminium, it is typically 650degC and 750degC. It is necessary to keep the melt clean. The impurities are eliminated by the operator with the help of fluxing agents and skimming tools. In case some oxide or gas is left, it may introduce defects such as porosity or inclusions in the future. In high-tech furnaces, a dosing system is the direct connection between the furnace and a die casting machine of China Cold. This guarantees that the temperature and composition of the molten metal are uniform in each shot. Molten Metal to the Shot Chamber Then molten metal is poured into the shot chamber or shot sleeve. This may be done manually or automatically. Manual ladling is easy, less fast and has more chances of entraping air. Automatic ladling systems, in their turn, provide the accurate amounts of metal with low turbulence. Oxidation and gas inclusion can be prevented by controlling the ladling speed and temperature. Others preheat the shot sleeve a little so that it will not suddenly drop in temperature, to allow the fluidity of injection. 3. Injection into the Die Cavity A hydraulic plunger is used to inject the high-pressure molten metal into the die cavity once it is in the shot sleeve. This is the fundamental phase of the cold chamber die casting. Injection pressure varies between 3,000 psi and more than 20,000 psi, depending on the size of the part and the alloy. The injection cycle normally contains two stages: The timeliness of these phases is critical. Recent China cold chamber die casting machinery, servo-hydraulic systems automatically regulate pressure and speed of every shot and guarantee homogeneity. Solidification and Cooling Opening and Part Ejection Die Once the metal has solidified, the die is opened by the machine, after which ejector pins or robotic arms take the casting out. It should be ejected only when fully solidified; otherwise, it is distorted. In complex shapes, there is more than one ejector pin, which guarantees the clean release of the die cavity. Robots take the parts on the automated lines and place them on conveyors to be trimmed and cooled. This increases handling damage reduction and accelerates production. Trimming and Finishing Inspection and Quality Control The last one is inspection and quality control. Every casting is inspected to guarantee that it has the necessary tolerances and quality standards. Popular types of inspection are: The machinery of modern China cold chamber die casting is usually equipped with sensors and software which keep track of all the parameters – Melt temperature, injection pressure, and die temperature, which enables quality monitoring in real time. Optimisation of process and control The quality of outcomes must rely on controlled quality at each step. Safety and Environmental Factors Usually used materials and alloys. The use of a cold chamber is preferred in alloys which cannot be utilised in hot-chamber machines. Most common materials used include aluminium alloys, magnesium, copper and a few combinations of zinc andaluminiumm where corrosion of the injection mechanism should be prevented at all costs. In the automotive structural parts, aluminium alloys prevail. Magnesium is applicable in situations where very lightness is an issue. Both alloys have their own melting point, fluidity and shrinkage behaviour, which need to be handled in mould design and process parameters. Machinery and features – such as the China cold chamber die casting machine choice. Die casting machines: The Cold chamber die casting machines are made of a robust frame, high pressure injection unit, a hydraulic system and the control electronics. The modern machines provide servo-hydraulics to save energy and enhance control, computer controls to make the shot profiles programmable and integrated auxiliary systems such as die temperature controllers and automatic ladling systems. It is also possible to find China cold chamber die casting machine suppliers that offer a large variety of models and different price ranges in case you are sourcing machines. There are compact models of Chinese manufacturers that fit small shops and large tonnage machines that are appropriate to high-volume production. Chinese constructors tend to package melting and handling equipment to provide a turnkey line as well. Compare machines in terms of check maximum clamping force (tons), volume in the shot, speed control in an injection, die size, and automation. Essentials of tooling and die design The hardened tool steel is normally die (mould. The design of the die should permit a controlled flow of metals and escaping gaseous air, and gating and runners geometry and cooling channels in order to