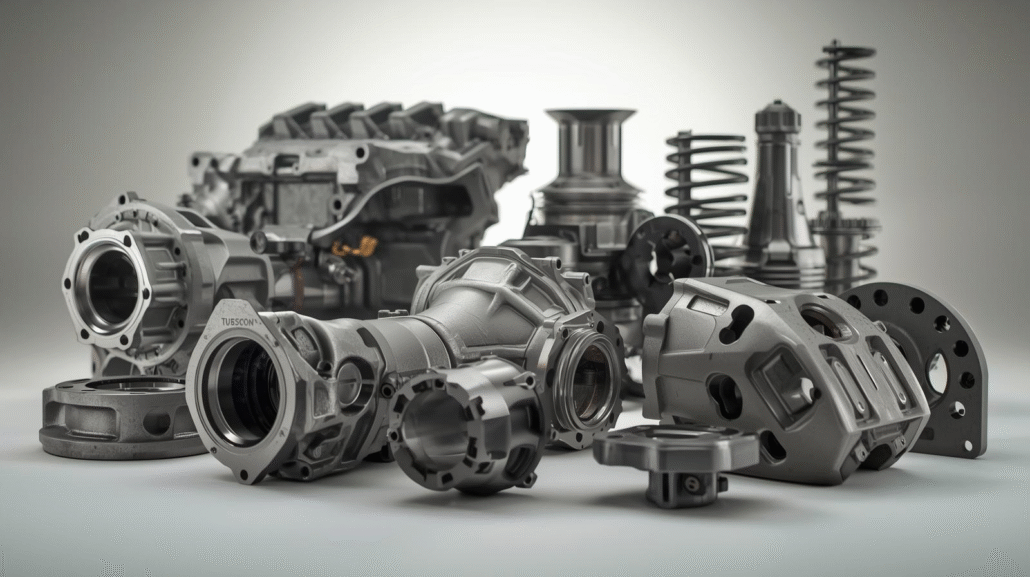
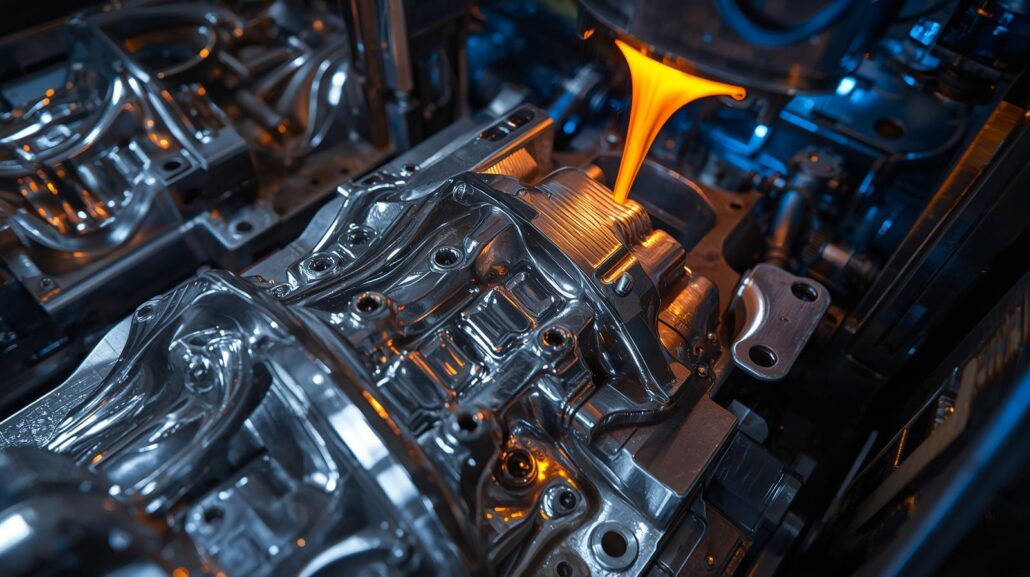
Top Automotive die casting companii din China și din lume
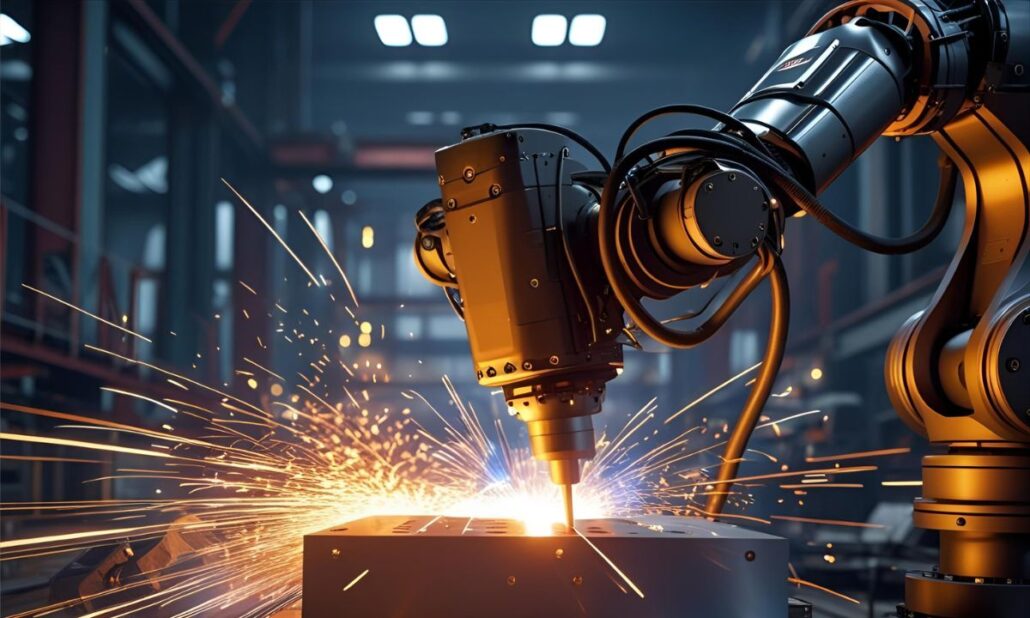
aluminiu turnat sub presiune, companii de turnare sub presiune, companie de turnare sub presiune, Die Casting ProducătorTurnarea aluminiului sub presiune este unul dintre cele mai fiabile și rentabile procese de fabricație din industria contemporană. Acesta este procesul de injectare la presiune ridicată a aluminiului topit la temperatură ridicată într-o matriță precisă pentru a crea piese puternice, ușoare și precise din punct de vedere dimensional. Este deosebit de util în producția de forme foarte complexe cu finisaje de suprafață ridicate și, prin urmare, este un proces favorizat în industria auto, aerospațială, electronică, a produselor de consum și a utilajelor industriale. Turnarea sub presiune a aluminiului a fost la mare căutare în ultimii ani. Tendința lumii către mașini electrice, construcții ușoare și eficiență energetică a plasat aliajele de aluminiu în prima linie a inovării. Producătorii au dezvoltat acum componente de înaltă tehnologie, cum ar fi blocuri motor, case de transmisie, carcase de baterii și radiatoare, care sunt atât durabile, cât și ușoare. Reciclabilitatea și rezistența la coroziune fac ca aluminiul să fie util și în tendințele mondiale de a produce durabil și ecologic. Două dintre principalele centre de turnare sub presiune a aluminiului sunt Statele Unite ale Americii și China. Companiile din Statele Unite sunt cunoscute ca fiind inovatoare, au standarde ridicate de calitate și utilizează niveluri ridicate de automatizare și pot fi considerate o investiție bună în industriile de înaltă precizie. În schimb, producătorii chinezi au câștigat multă competitivitate pe piața mondială, au oferit o soluție rentabilă, o capacitate de producție ridicată și tehnologii mai avansate. Această lucrare va discuta despre unele dintre cele mai de succes industrii de turnare sub presiune a aluminiului din SUA și China, punctele lor forte, abilitățile și factorii care le fac cei mai de încredere parteneri pe care întreprinderile din întreaga lume îi consideră furnizorii lor preferați în industria prelucrătoare. Ce este turnarea sub presiune a automobilelor? Turnarea sub presiune este un proces de producție prin care metalul topit, de obicei aluminiu, magneziu sau zinc, este forțat sub presiune mare într-o matriță care are un spațiu deschis. Acest lucru permite producția în masă de componente de înaltă rezistență cu funcții complexe și cu o bună finisare a suprafeței și precizie dimensională. Turnarea sub presiune în industria automobilelor permite producția de componente care sunt: Utilizarea turnării sub presiune a revoluționat construcția vehiculelor contemporane, prin care se poate economisi greutate și, în același timp, se pot obține performanțe. Cererea a contribuit la rata ridicată de dezvoltare a principalelor întreprinderi de turnare sub presiune a automobilelor din China, Europa, America și Japonia. De ce China este lider în domeniul turnării sub presiune a automobilelor China are unele dintre cele mai mari întreprinderi din lume producătoare de piese turnate sub presiune pentru automobile, datorită caracteristicilor sale: Un astfel de set de puncte forte a permis firmelor chineze de turnare sub presiune a automobilelor să fie puternice nu numai pe piața locală, ci și la nivel internațional în lanțul de aprovizionare. CNM Tech Diecasting Company este un producător de top de produse superioare din aluminiu turnat sub presiune. Acestea oferă mai multor sectoare, cum ar fi cel auto, electronic și al telecomunicațiilor, componente proiectate cu precizie care vizează menținerea celor mai înalte standarde de calitate. Ei pot produce piese ușoare și puternice utilizând procesele lor avansate de producție, cum ar fi turnarea sub presiune de înaltă presiune și prelucrarea CNC. The Diecasting Company crede în puterea inovației constante și, prin urmare, investește în utilaje moderne, linii de producție automatizate și, mai important, sisteme de control al calității care ajută la obținerea acelorași rezultate în orice moment. Atât OEM-urile, cât și furnizorii Tier-1 fac parte din baza lor globală de clienți și, prin urmare, sunt un partener de încredere în satisfacerea nevoilor de producție complexe și de volum mare. Website: https://www.thediecasting.com/ De ce să îi alegeți The Diecasting Company este preferată de întreprinderi deoarece se concentrează pe calitate, precizie și inovare. Aplicarea tehnologiilor de turnare sub presiune de ultimă generație, controlul riguros al calității și livrarea la timp fac ca clienții lor să primească componente care ar putea îndeplini standardele internaționale și îi fac alegerea preferată atunci când vine vorba de OEM-uri și producători auto care doresc să găsească un furnizor de soluții fiabile de turnare sub presiune. Industrii deservite Sincere Tech Sincere Tech este unul dintre producătorii de matrițe de înaltă precizie în injecția de plastic și turnare sub presiune. Ei au o experiență în proiectarea matrițelor, prototiparea și fabricarea produsului final, care oferă o soluție unică clienților lor din întreaga lume. Ei folosesc software computerizat CAD / CAM și prelucrare automată, astfel încât toate matrițele fabricate sunt foarte precise. Plastic Mold poate fi creditat cu ani de experiență în satisfacerea nevoilor industriilor de automobile, electronice de consum și dispozitive medicale cu capacitatea de a livra matrițe complexe cu eficiență. Aceștia se remarcă prin inovație, control al calității și rapiditate în livrare, devenind astfel un furnizor de încredere al companiilor care doresc să aibă o soluție de matrițe personalizate. Website: https://www.plasticmold.net/ Why Choose Them Plastic Mold este selectat datorită sistemelor lor complete de fabricare a matrițelor, competențelor tehnice și capacității de a se încadra în timpul de producție limitat. Matrițele lor de calitate superioară minimizează erorile, sporesc productivitatea și ajută clienții să aibă produse turnate sub presiune sau turnate prin injecție precise și fiabile. Industriile deservite GC Precision Mould GC Precision Mould este un producător de piese turnate sub presiune din China care furnizează piese turnate sub presiune din aluminiu, zinc și magneziu. Ei au reputația de a produce piese de înaltă calitate, rentabile și ușoare în sectoarele auto, electronic și de iluminat. Ei au abilitățile de turnare sub presiune înaltă, prelucrare CNC și operațiuni secundare de finisare. Alu Diecasting se concentrează pe precizie, longevitate și productivitate. Aceștia sunt întotdeauna la înălțimea standardelor internaționale prin utilizarea de facilități moderne, linii automatizate și ingineri calificați. Ei se adresează clienților atât la nivel local, cât și la nivel internațional, cum ar fi OEM-urile și furnizorii Tier-1, și sunt poziționați ca un producător chinez de top de piese turnate sub presiune ca o industrie auto. Site web: https://aludiecasting.com/ De ce să îi alegeți Ei folosesc Alu Diecasting deoarece oferă o combinație de prețuri competitive, standarde de înaltă calitate și tehnologie. Ei au un istoric de diverse aliaje, prelucrare de precizie și producție la timp, care menține piese fiabile, cu durată lungă de viață și ușoare, care satisfac cerințele industriei auto mondiale. Industrii deservite Get It Made Get It Made este un producător de prelucrare CNC, imprimare 3D, turnare sub presiune și formare de metale cu sediul în Regatul Unit. Aceștia sprijină atât prototiparea, cât și producția de volum redus,